Comparison of patient reported quality of life and impact of treatment side effects experienced with a taxane-containing regimen and standard anthracycline based chemotherapy for early breast cancer: 6 year results from the UK TACT trial (CRUK/01/001)
- PMID: 25065293
- PMCID: PMC4166460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.06.007
Comparison of patient reported quality of life and impact of treatment side effects experienced with a taxane-containing regimen and standard anthracycline based chemotherapy for early breast cancer: 6 year results from the UK TACT trial (CRUK/01/001)
Abstract
Background: The TACT trial (CRUK/01/001) compared adjuvant sequential FEC-docetaxel (FEC-D) chemotherapy with standard anthracycline-based chemotherapy of similar duration in women with early breast cancer. Results at a median of 5 years suggested no improvement in disease-free survival with FEC-D. Given differing toxicity profiles of the regimens, the impact on quality of life (QL) was explored.
Methods: Patients from 44 centres completed standardised QL questionnaires before chemotherapy, after cycles 4 and 8, at 9, 12, 18 and 24 months and at 6 years follow-up. Patient diaries assessed frequency, associated distress and impact on daily activity of 15 treatment related side effects.
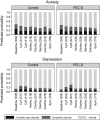
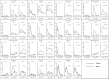
Findings: 830 patients (415 FEC-D; 415 controls) contributed assessments during 0-24 months; 362 of whom participated again at 6 years. During chemotherapy, FEC-D impaired global health/QL and depression rates and significantly more QL domains than standard regimens. Novel diary card ratings highlighted significantly more distress and interference with daily activities due to FEC-D side effects compared with standard treatment. In both groups, most QL parameters returned to baseline levels by 2 years and were unchanged at 6 years.
Interpretation: Within expected negative effects of chemotherapy on wide ranging QL domains FEC-D patients reported greater toxicity, disruption and distress during treatment with no improvement in disease outcome at 5 years than patients receiving standard anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Findings should inform future patients of relative costs and benefits of adjuvant chemotherapy.
Keywords: Breast; Chemotherapy; Early; Patient reported outcomes; Quality of life; Randomised controlled trial.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Peto R., Davies C., Godwin J., Gray R., Pan H.C. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012;379(9914):432–444. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Francis P., Crown J., Di Leo A., Buyse M., Balil A., Andersson M., BIG 02-98 Collaborative Group Adjuvant chemotherapy with sequential or concurrent anthracycline and docetaxel: Breast International Group 02–98 randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:121–133. - PubMed
-
- Jones S., Holmes F.A., O’Shaughnessy J., Blum J.L., Vukelja S.J., McIntyre K.J. Docetaxel with cyclophosphamide is associated with an overall survival benefit compared with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide: 7 year follow-up of US Oncology Research Trial 9735. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1177–1183. - PubMed
-
- Mamounas E.P., Bryant J., Lembersky B., Fehrenbacher L., Sedlacek S.M., Fisher B. Paclitaxel after doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: results from NSABP B28. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(16):3686–3696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

