GABAB receptor phosphorylation regulates KCTD12-induced K⁺ current desensitization
- PMID: 25065880
- PMCID: PMC4402209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.07.013
GABAB receptor phosphorylation regulates KCTD12-induced K⁺ current desensitization
Abstract
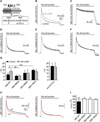
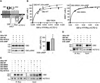
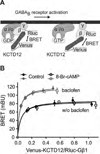
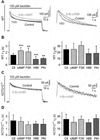
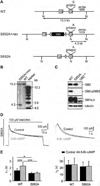
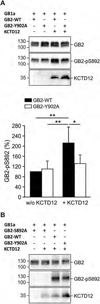
GABAB receptors assemble from GABAB1 and GABAB2 subunits. GABAB2 additionally associates with auxiliary KCTD subunits (named after their K(+) channel tetramerization-domain). GABAB receptors couple to heterotrimeric G-proteins and activate inwardly-rectifying K(+) channels through the βγ subunits released from the G-protein. Receptor-activated K(+) currents desensitize in the sustained presence of agonist to avoid excessive effects on neuronal activity. Desensitization of K(+) currents integrates distinct mechanistic underpinnings. GABAB receptor activity reduces protein kinase-A activity, which reduces phosphorylation of serine-892 in GABAB2 and promotes receptor degradation. This form of desensitization operates on the time scale of several minutes to hours. A faster form of desensitization is induced by the auxiliary subunit KCTD12, which interferes with channel activation by binding to the G-protein βγ subunits. Here we show that the two mechanisms of desensitization influence each other. Serine-892 phosphorylation in heterologous cells rearranges KCTD12 at the receptor and slows KCTD12-induced desensitization. Likewise, protein kinase-A activation in hippocampal neurons slows fast desensitization of GABAB receptor-activated K(+) currents while protein kinase-A inhibition accelerates fast desensitization. Protein kinase-A fails to regulate fast desensitization in KCTD12 knock-out mice or knock-in mice with a serine-892 to alanine mutation, thus demonstrating that serine-892 phosphorylation regulates KCTD12-induced desensitization in vivo. Fast current desensitization is accelerated in hippocampal neurons carrying the serine-892 to alanine mutation, showing that tonic serine-892 phosphorylation normally limits KCTD12-induced desensitization. Tonic serine-892 phosphorylation is in turn promoted by assembly of receptors with KCTD12. This cross-regulation of serine-892 phosphorylation and KCTD12 activity sharpens the response during repeated receptor activation.
Keywords: G-protein coupled receptor; GABA-B; GPCR; Kir3; PKA.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Gassmann M, Bettler B. Regulation of neuronal GABAB receptor functions by subunit composition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:380–394. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Mosbacher J, Gassmann M. Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABAB receptors. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:835–867. - PubMed
-
- Couve A, Moss SJ, Pangalos MN. GABAB receptors: a new paradigm in G protein signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000;16:296–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

