Central role of soluble adenylyl cyclase and cAMP in sperm physiology
- PMID: 25066614
- PMCID: PMC4262597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.07.013
Central role of soluble adenylyl cyclase and cAMP in sperm physiology
Abstract
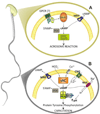
Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP), the first second messenger to be described, plays a central role in cell signaling in a wide variety of cell types. Over the last decades, a wide body of literature addressed the different roles of cAMP in cell physiology, mainly in response to neurotransmitters and hormones. cAMP is synthesized by a wide variety of adenylyl cyclases that can generally be grouped in two types: transmembrane adenylyl cyclase and soluble adenylyl cyclases. In particular, several aspects of sperm physiology are regulated by cAMP produced by a single atypical adenylyl cyclase (Adcy10, aka sAC, SACY). The signature that identifies sAC among other ACs, is their direct stimulation by bicarbonate. The essential nature of cAMP in sperm function has been demonstrated using gain of function as well as loss of function approaches. This review unifies state of the art knowledge of the role of cAMP and those enzymes involved in cAMP signaling pathways required for the acquisition of fertilizing capacity of mammalian sperm. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: The role of soluble adenylyl cyclase in health and disease.
Keywords: Soluble adenylyl cyclase; Sperm capacitation; Transmembrane adenylyl cyclase; cAMP.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sutherland EW, Rall TW. Fractionation and Characterization of a Cyclic Adenine Ribonucleotide Formed by Tissue Particles. J. Biol. Chem. 1958;232:1077–1091. - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki H, Springett GM, Mochizuki N, Toki S, Nakaya M, Matsuda M, Housman DE, Graybiel AM. A Family of CAMP-Binding Proteins That Directly Activate Rap1. Science. 1998;282:2275–2279. - PubMed
-
- de Rooij J, Zwartkruis FJ, Verheijen MH, Cool RH, Nijman SM, Wittinghofer A, Bos JL. Epac Is a Rap1 Guanine-Nucleotide-Exchange Factor Directly Activated by Cyclic AMP. Nature. 1998;396:474–477. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig J, Margalit T, Eismann E, Lancet D, Kaupp UB. Primary Structure of CAMP-Gated Channel From Bovine Olfactory Epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1990;270:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Dessauer CW, Scully TT, Gilman AG. Interactions of Forskolin and ATP With the Cytosolic Domains of Mammalian Adenylyl Cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:22272–22277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

