Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: functional links and key pathways
- PMID: 25066777
- PMCID: PMC4306641
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.27332
Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: functional links and key pathways
Abstract
Inflammation is one of the most characteristic features of chronic liver disease of viral, alcoholic, fatty, and autoimmune origin. Inflammation is typically present in all disease stages and associated with the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. In the past decade, numerous studies have contributed to improved understanding of the links between hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. Here, we review mechanisms that link inflammation with the development of liver fibrosis, focusing on the role of inflammatory mediators in hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and HSC survival during fibrogenesis and fibrosis regression. We will summarize the contributions of different inflammatory cells, including hepatic macrophages, T and B lymphocytes, natural killer cells and platelets, as well as key effectors, such as cytokines, chemokines, and damage-associated molecular patterns. Furthermore, we will discuss the relevance of inflammatory signaling pathways for clinical liver disease and for the development of antifibrogenic strategies.
© 2014 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
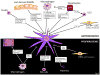
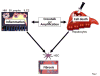
References
-
- Canbay A, Taimr P, Torok N, Higuchi H, Friedman S, Gores GJ. Apoptotic body engulfment by a human stellate cell line is profibrogenic. Lab Invest. 2003;83:655–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AA021912/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020211/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5P42ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020172/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085252/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AA02017204/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076920/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK085252/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01AA021912/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK076920/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AA020211/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
