Focal liver lesions detection and characterization: The advantages of gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MRI
- PMID: 25067999
- PMCID: PMC4110539
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i7.477
Focal liver lesions detection and characterization: The advantages of gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MRI
Abstract
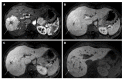
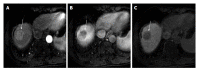
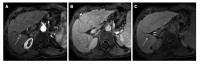
Since its clinical introduction, several studies in literature have investigated gadolinium ethoxybenzhyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid or gadoxetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) properties. Following contrast injection, it provides dynamic vascular phases (arterial, portal and equilibrium phases) and hepatobiliary phase, the latter due to its uptake by functional hepatocytes. The main advantages of Gd-EOB-DTPA of focal liver lesion detection and characterization are discussed in this paper. Namely, we focus on the possibility of distinguishing focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) from hepatic adenoma (HA), the identification of early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the pre-operative assessment of metastasis in liver parenchyma. Regarding the differentiation between FNH and HA, adenoma typically appears hypointense in hepatobiliary phase, whereas FNH is isointense or hyperintense to the surrounding hepatic parenchyma. As for the identification of early HCCs, many papers recently published in literature have emphasized the contribution of hepatobiliary phase in the characterization of nodules without a typical hallmark of HCC. Atypical nodules (no hypervascularizaton observed on arterial phase and/or no hypovascular appearance on portal phase) with low signal intensity in the hepatobiliary phase, have a high probability of malignancy. Finally, regarding the evaluation of focal hepatic metastases, magnetic resonance pre-operative assessment using gadoxetic acid allows for more accurate diagnosis.
Keywords: Carcinoma; Gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid; Hepatocellular; Image enhancement; Liver; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Weinmann HJ, Schuhmann-Giampieri G, Schmitt-Willich H, Vogler H, Frenzel T, Gries H. A new lipophilic gadolinium chelate as a tissue-specific contrast medium for MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1991;22:233–237; discussion 242. - PubMed
-
- Schuhmann-Giampieri G, Schmitt-Willich H, Press WR, Negishi C, Weinmann HJ, Speck U. Preclinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a contrast agent in MR imaging of the hepatobiliary system. Radiology. 1992;183:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Clément O, Mühler A, Vexler V, Berthezène Y, Brasch RC. Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-DTPA, a new liver-specific magnetic resonance contrast agent. Kinetic and enhancement patterns in normal and cholestatic rats. Invest Radiol. 1992;27:612–619. - PubMed
-
- Clément O, Mühler A, Vexler VS, Rosenau W, Berthezène Y, Kuwatsuru R, Brasch RC. Evaluation of radiation-induced liver injury with MR imaging: comparison of hepatocellular and reticuloendothelial contrast agents. Radiology. 1992;185:163–168. - PubMed
-
- Mühler A, Clément O, Vexler V, Berthezène Y, Rosenau W, Brasch RC. Hepatobiliary enhancement with Gd-EOB-DTPA: comparison of spin-echo and STIR imaging for detection of experimental liver metastases. Radiology. 1992;184:207–213. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

