Neuroimaging essentials in essential tremor: a systematic review
- PMID: 25068111
- PMCID: PMC4110352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.05.003
Neuroimaging essentials in essential tremor: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Essential tremor is regarded to be a disease of the central nervous system. Neuroimaging is a rapidly growing field with potential benefits to both diagnostics and research. The exact role of imaging techniques with respect to essential tremor in research and clinical practice is not clear. A systematic review of the different imaging techniques in essential tremor is lacking in the literature.
Methods: We performed a systematic literature search combining the terms essential tremor and familial tremor with the following keywords: imaging, mri, vbm, dwi, fmri, pet and spect, both in abbreviated form as well as in full form. We summarize and discuss the quality and the external validity of each study and place the results in the context of existing knowledge regarding the pathophysiology of essential tremor.
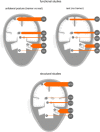
Results: A total of 48 neuroimaging studies met our search criteria, roughly divided into 19 structural and 29 functional and metabolic studies. The quality of the studies varied, especially concerning inclusion criteria. Functional imaging studies indicated cerebellar hyperactivity during rest and during tremor. The studies also pointed to the involvement of the thalamus, the inferior olive and the red nucleus. Structural studies showed less consistent results.
Discussion and conclusion: Neuroimaging techniques in essential tremor give insight into the pathophysiology of essential tremor indicating the involvement of the cerebellum as the most consistent finding. GABAergic dysfunction might be a major premise in the pathophysiological hypotheses. Inconsistencies between studies can be partly explained by the inclusion of heterogeneous patient groups. Improvement of scientific research requires more stringent inclusion criteria and application of advanced analysis techniques. Also, the use of multimodal neuroimaging techniques is a promising development in movement disorders research. Currently, the role of imaging techniques in essential tremor in daily clinical practice is limited.
Keywords: DWI, diffusion weighted imaging; Essential tremor; MRI; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; Neuroimaging; PET, positron emission tomography; Pathophysiology; Review; SPECT, single-photon emission computed tomography; Scintigraphy; VBM, voxel-based morphometry; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Andersen A.R. 99mTc-D,L-hexamethylene-propyleneamine oxime (99mTc-HMPAO): basic kinetic studies of a tracer of cerebral blood flow. Cerebrovascular and Brain Metabolism Reviews. 1989;1:288–318. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2701656 - PubMed
-
- Antonini A., Moresco R.M., Gobbo C., De N.R., Panzacchi A., Barone P., Calzetti S., Negrotti A., Pezzoli G., Fazio F. The status of dopamine nerve terminals in Parkinson's disease and essential tremor: a PET study with the tracer [11-C]FE-CIT. Neurological Sciences: Official Journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2001;22:47–48. 11487195 - PubMed
-
- Bagepally B.S., Bhatt M.D., Chandran V., Saini J., Bharath R.D., Vasudev M.K., Prasad C., Yadav R., Pal P.K. Decrease in cerebral and cerebellar gray matter in essential tremor: a voxel-based morphometric analysis under 3 T MRI. Journal of Neuroimaging: Official Journal of the American Society of Neuroimaging. 2012;22:275–278. 21447032 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

