Characterization of amniotic stem cells
- PMID: 25068631
- PMCID: PMC4116113
- DOI: 10.1089/cell.2013.0090
Characterization of amniotic stem cells
Abstract
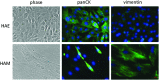
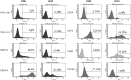
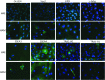
The amnion membrane is developed from embryo-derived cells, and amniotic cells have been shown to exhibit multidifferentiation potential. These cells represent a desirable source for stem cells for a variety of reasons. However, to date very few molecular analyses of amnion-derived cells have been reported, and efficient markers for isolating the stem cells remain unclear. This paper assesses the characterization of amnion-derived cells as stem cells by examining stemness marker expressions for amnion-derived epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells by flow cytometry, immunocytochemistry, and quantitative PCR. Flow cytometry revealed that amnion epithelial cells expressed CD133, CD 271, and TRA-1-60, whereas mecenchymal cells expressed CD44, CD73, CD90, and CD105. Immunohistochemistry showed that both cells expressed the stemness markers Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4, and SSEA4. Stemness genes' expression in amnion epithelial cells, mesenchymal cells, fibroblast, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) was compared by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Amnion-derived epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells expressed Oct3/4, Nanog, and Klf4 more than bone marrow-derived MSCs. The sorted TRA1-60-positive cells expressed Oct3/4, Nanog, and Klf4 more than unsorted cells or TRA1-60-negative cells. TRA1-60 can be a marker for isolating amnion epithelial stem cells.
Figures


References
-
- Adinolfi M., Akle C.A., McColl I., Fensom A.H., Tansley L., Connolly P., His B.L., Faulk W.P., Travers P., and Bodmer F.W. (1982). Expression of HLA antigens, beta 2-microglobulin and enzymes by human amniotic epithelial cells. Nature, 295, 325–327 - PubMed
-
- Akle C.A., Adinolfi M., Welsh K.L., Leibowitz S., and McColl I. (1981). Immunogenicity of human amniotic epithelial cells after transplantation into volunteers. Lancet, 2, 1003–1005 - PubMed
-
- Bilic G., Zeisberger S.M., Mallik A.S, Zimmermann R., and Zisch A.H. (2008). Comparative caracherization of cultured human term amnion epithelial and mesenchymal stromal cells for application in cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 17, 955–968 - PubMed
-
- Cargnoni A., Gibelli L., Tosini A., Signoroni P.B., Nassuato C., Arienti D., Lombardi G, Alberini A., Wengler G.S., and Perolini O. (2009). Transplantation of allogenic and xenogenic placenta-derived cells reduces bleomycine-induced lung fibrosis. Cell Transplant. 18, 405–422 - PubMed
-
- Cargnoni A., Piccinelli E.C., Ressel L., Rossi D., Magatti M., Tosci I., Cesari V., Albertini M., Mazzola S., and Parolini O. (2014). Conditioned medium from amniotic membrane-derived cells prevents lung fibrosis and preserves blood gas exchanges in bleomycin-injured mice—specificity of the effects and insights into possible mechanisms. Cytotherapy 16, 17–32 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

