Mitochondria are gate-keepers of T cell function by producing the ATP that drives purinergic signaling
- PMID: 25070895
- PMCID: PMC4162192
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.575308
Mitochondria are gate-keepers of T cell function by producing the ATP that drives purinergic signaling
Abstract
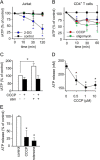
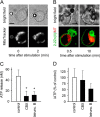
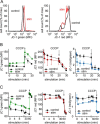
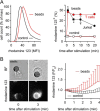
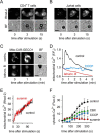
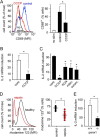
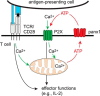
T cells play a central role in host defense. ATP release and autocrine feedback via purinergic receptors has been shown to regulate T cell function. However, the sources of the ATP that drives this process are not known. We found that stimulation of T cells triggers a spike in cellular ATP production that doubles intracellular ATP levels in <30 s and causes prolonged ATP release into the extracellular space. Cell stimulation triggered rapid mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake, increased oxidative phosphorylation, a drop in mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm), and the accumulation of active mitochondria at the immune synapse of stimulated T cells. Inhibition of mitochondria with CCCP, KCN, or rotenone blocked intracellular ATP production, ATP release, intracellular Ca(2+) signaling, induction of the early activation marker CD69, and IL-2 transcription in response to cell stimulation. These findings demonstrate that rapid activation of mitochondrial ATP production fuels the purinergic signaling mechanisms that regulate T cells and define their role in host defense.
Keywords: ATP; Calcium; Cellular Immune Response; Immunosuppression; Infectious Disease; Inflammation; Purinergic Receptor; Purinergic Signaling; T Cell.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Schenk U., Westendorf A. M., Radaelli E., Casati A., Ferro M., Fumagalli M., Verderio C., Buer J., Scanziani E., Grassi F. (2008) Purinergic control of T cell activation by ATP released through pannexin-1 hemichannels. Sci. Signal 1, ra6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

