FANCD2 re-expression is associated with glioma grade and chemical inhibition of the Fanconi Anaemia pathway sensitises gliomas to chemotherapeutic agents
- PMID: 25071006
- PMCID: PMC4171640
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2225
FANCD2 re-expression is associated with glioma grade and chemical inhibition of the Fanconi Anaemia pathway sensitises gliomas to chemotherapeutic agents
Abstract
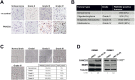
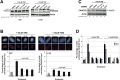
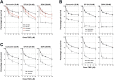
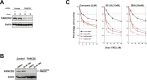
Brain tumours kill more children and adults under 40 than any other cancer. Around half of primary brain tumours are glioblastoma multiforme (GBMs) where treatment remains a significant challenge, where survival rates have improved little over the last 40 years, thus highlighting an unmet need for the identification/development of novel therapeutic targets and agents to improve GBM treatment. Using archived and fresh glioma tissue, we show that in contrast to normal brain or benign schwannomas GBMs exhibit re-expression of FANCD2, a key protein of the Fanconi Anaemia (FA) DNA repair pathway, and possess an active FA pathway. Importantly, FANCD2 expression levels are strongly associated with tumour grade, revealing a potential exploitable therapeutic window to allow inhibition of the FA pathway in tumour cells, whilst sparing normal brain tissue. Using several small molecule inhibitors of the FA pathway in combination with isogenic FA-proficient/deficient glioma cell lines as well as primary GBM cultures, we demonstrate that inhibition of the FA pathway sensitises gliomas to the chemotherapeutic agents Temozolomide and Carmustine. Our findings therefore provide a strong rationale for the development of novel and potent inhibitors of the FA pathway to improve the treatment of GBMs, which may ultimately impact on patient outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adamson C, Kanu OO, Mehta AI, Di C, Lin N, Mattox AK, Bigner DD. Glioblastoma multiforme: a review of where we have been and where we are going. Expert opinion on investigational drugs. 2009;18(8):1061–1083. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444(7120):756–760. - PubMed
-
- Johannessen TC, Bjerkvig R, Tysnes BB. DNA repair and cancer stem-like cells--potential partners in glioma drug resistance? Cancer treatment reviews. 2008;34(6):558–567. - PubMed
-
- Crossan GP, Patel KJ. The Fanconi anaemia pathway orchestrates incisions at sites of crosslinked DNA. The Journal of pathology. 2012;226(2):326–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

