p66ShcA promotes breast cancer plasticity by inducing an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 25071152
- PMCID: PMC4187732
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00341-14
p66ShcA promotes breast cancer plasticity by inducing an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
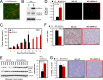
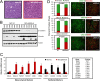
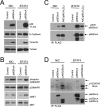
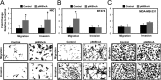
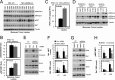
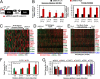
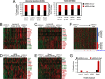
Breast cancers are stratified into distinct subtypes, which influence therapeutic responsiveness and patient outcome. Patients with luminal breast cancers are often associated with a better prognosis relative to that with other subtypes. However, subsets of patients with luminal disease remain at increased risk of cancer-related death. A critical process that increases the malignant potential of breast cancers is the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). The p66ShcA adaptor protein stimulates the formation of reactive oxygen species in response to stress stimuli. In this paper, we report a novel role for p66ShcA in inducing an EMT in HER2(+) luminal breast cancers. p66ShcA increases the migratory properties of breast cancer cells and enhances signaling downstream of the Met receptor tyrosine kinase in these tumors. Moreover, Met activation is required for a p66ShcA-induced EMT in luminal breast cancer cells. Finally, elevated p66ShcA levels are associated with the acquisition of an EMT in primary breast cancers spanning all molecular subtypes, including luminal tumors. This is of high clinical relevance, as the luminal and HER2 subtypes together comprise 80% of all newly diagnosed breast cancers. This study identifies p66ShcA as one of the first prognostic biomarkers for the identification of more aggressive tumors with mesenchymal properties, regardless of molecular subtype.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. 2000. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752. 10.1038/35021093 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van't Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, Schreiber GJ, Peterse JL, Roberts C, Marton MJ, Parrish M, Atsma D, Witteveen A, Glas A, Delahaye L, van der Velde T, Bartelink H, Rodenhuis S, Rutgers ET, Friend SH, Bernards R. 2002. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 347:1999–2009. 10.1056/NEJMoa021967 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F, Speed T, Spellman PT, DeVries S, Lapuk A, Wang NJ, Kuo WL, Stilwell JL, Pinkel D, Albertson DG, Waldman FM, McCormick F, Dickson RB, Johnson MD, Lippman M, Ethier S, Gazdar A, Gray JW. 2006. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 10:515–527. 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
