KCNJ10 determines the expression of the apical Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) in the early distal convoluted tubule (DCT1)
- PMID: 25071208
- PMCID: PMC4136599
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1411705111
KCNJ10 determines the expression of the apical Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) in the early distal convoluted tubule (DCT1)
Abstract
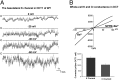
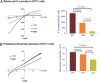
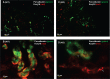
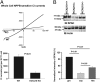
The renal phenotype induced by loss-of-function mutations of inwardly rectifying potassium channel (Kir), Kcnj10 (Kir4.1), includes salt wasting, hypomagnesemia, metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia. However, the mechanism by which Kir.4.1 mutations cause the tubulopathy is not completely understood. Here we demonstrate that Kcnj10 is a main contributor to the basolateral K conductance in the early distal convoluted tubule (DCT1) and determines the expression of the apical Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) in the DCT. Immunostaining demonstrated Kcnj10 and Kcnj16 were expressed in the basolateral membrane of DCT, and patch-clamp studies detected a 40-pS K channel in the basolateral membrane of the DCT1 of p8/p10 wild-type Kcnj10(+/+) mice (WT). This 40-pS K channel is absent in homozygous Kcnj10(-/-) (knockout) mice. The disruption of Kcnj10 almost completely eliminated the basolateral K conductance and decreased the negativity of the cell membrane potential in DCT1. Moreover, the lack of Kcnj10 decreased the basolateral Cl conductance, inhibited the expression of Ste20-related proline-alanine-rich kinase and diminished the apical NCC expression in DCT. We conclude that Kcnj10 plays a dominant role in determining the basolateral K conductance and membrane potential of DCT1 and that the basolateral K channel activity in the DCT determines the apical NCC expression possibly through a Ste20-related proline-alanine-rich kinase-dependent mechanism.
Keywords: Kir.5.1; SPAK; SeSAME/EAST syndrome; WNK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 Deficiency Inhibits the Basolateral K+ Channels in the Distal Convoluted Tubule and Impairs Renal K+ and Mg2+ Transport.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Nov;26(11):2678-90. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014070658. Epub 2015 Apr 6. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25848073 Free PMC article.
-
Src family protein tyrosine kinase regulates the basolateral K channel in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) by phosphorylation of KCNJ10 protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):26135-26146. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.478453. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23873931 Free PMC article.
-
Kir4.1/Kir5.1 of distal convoluted tubule is required for short-term angiotensin-II-induced stimulation of Na-Cl cotransporter.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Jun 1;328(6):F775-F786. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00004.2025. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40241495
-
Basolateral Kir4.1 activity in the distal convoluted tubule regulates K secretion by determining NaCl cotransporter activity.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Sep;25(5):429-35. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000248. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27306796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression, regulation, and function of Kir4.1 (Kcnj10) in the mammalian kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):F12-5. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00112.2016. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27122539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating the multifaceted intricacies of the Na+-Cl- cotransporter, a highly regulated key effector in the control of hydromineral homeostasis.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jul 1;104(3):1147-1204. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2023. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38329422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two inwardly rectifying potassium channels, Irk1 and Irk2, play redundant roles in Drosophila renal tubule function.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Oct;309(7):R747-56. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00148.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26224687 Free PMC article.
-
In Primary Aldosteronism, Mineralocorticoids Influence Exosomal Sodium-Chloride Cotransporter Abundance.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Jan;28(1):56-63. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015111221. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27381844 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-calcium exchanger 1 is the key molecule for urinary potassium excretion against acute hyperkalemia.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 30;15(6):e0235360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235360. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32603346 Free PMC article.
-
The sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC) and epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) associate.Biochem J. 2016 Oct 1;473(19):3237-52. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160312. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27422782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Monroy A, Plata C, Hebert SC, Gamba G. Characterization of the thiazide-sensitive Na(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter: A new model for ions and diuretics interaction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;279(1):F161–F169. - PubMed
-
- Ellison DH, Valazquez H, Wright FS. Thiazide-sensitive sodium chloride cotransport in early distal tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1987;253(3 Pt 2):F546–F554. - PubMed
-
- Simon DB, et al. Gitelman’s variant of Bartter’s syndrome, inherited hypokalaemic alkalosis, is caused by mutations in the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter. Nat Genet. 1996;12(1):24–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

