Tracking orthographic learning in children with different profiles of reading difficulty
- PMID: 25071504
- PMCID: PMC4081833
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00468
Tracking orthographic learning in children with different profiles of reading difficulty
Abstract
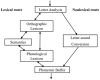
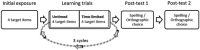
Previous studies have found that children with reading difficulties need more exposures to acquire the representations needed to support fluent reading than typically developing readers (e.g., Ehri and Saltmarsh, 1995). Building on existing orthographic learning paradigms, we report on an investigation of orthographic learning in poor readers using a new learning task tracking both the accuracy (untimed exposure duration) and fluency (200 ms exposure duration) of learning novel words over trials. In study 1, we used the paradigm to examine orthographic learning in children with specific poor reader profiles (nine with a surface profile, nine a phonological profile) and nine age-matched controls. Both profiles showed improvement over the learning cycles, but the children with surface profile showed impaired orthographic learning in spelling and orthographic choice tasks. Study 2 explored predictors of orthographic learning in a group of 91 poor readers using the same outcome measures as in Study 1. Consistent with earlier findings in typically developing readers, phonological decoding skill predicted orthographic learning. Moreover, orthographic knowledge significantly predicted orthographic learning over and beyond phonological decoding. The two studies provide insights into how poor readers learn novel words, and how their learning process may be compromised by less proficient orthographic and/or phonological skills.
Keywords: developmental dyslexia; orthographic knowledge; orthographic learning; phonological decoding; subtypes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orthographic learning in developmental surface and phonological dyslexia.Cogn Neuropsychol. 2015;32(2):58-79. doi: 10.1080/02643294.2014.1003536. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2015. PMID: 25639641
-
The use of orthographic and phonological strategies for the decoding of words in children with developmental dyslexia and average readers.Dyslexia. 2000 Oct-Dec;6(4):231-47. doi: 10.1002/1099-0909(200010/12)6:4<231::AID-DYS175>3.0.CO;2-3. Dyslexia. 2000. PMID: 11129450
-
Development of orthographic representations in Spanish children with dyslexia: the influence of previous semantic and phonological knowledge.Ann Dyslexia. 2019 Jul;69(2):186-203. doi: 10.1007/s11881-019-00178-6. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Ann Dyslexia. 2019. PMID: 30989486
-
Reading and reading-related skills in adults with dyslexia from different orthographic systems: a review and meta-analysis.Ann Dyslexia. 2020 Oct;70(3):339-368. doi: 10.1007/s11881-020-00205-x. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Ann Dyslexia. 2020. PMID: 32918699 Review.
-
Brain changes with Chinese reading development in typical and atypical readers.Front Psychol. 2023 Nov 21;14:1292985. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1292985. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38078252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orthographic learning in adults through overt and covert reading.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2023 Nov;241:104061. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2023.104061. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37924575 Free PMC article.
-
Novel reading index for identifying disordered reading skill development: A preliminary study.Appl Neuropsychol Child. 2018 Oct-Dec;7(4):287-297. doi: 10.1080/21622965.2017.1328681. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Appl Neuropsychol Child. 2018. PMID: 28569544 Free PMC article.
-
Orthographic learning in children with isolated and combined reading and spelling deficits.Child Neuropsychol. 2019 Apr;25(3):370-393. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2018.1470611. Epub 2018 May 7. Child Neuropsychol. 2019. PMID: 29732940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams C., Cooke R., Crutchley A., Hesketh A., Reeves D. (2001). Assessment of Comprehension and Expression 6-11 (ACE6-11). Windsor: Nelson Publishing Company Ltd
-
- Baayen R. H, Piepenbrock R., van Rijn H. (1993). The CELEX Lexical Database (CD-ROM). Philadelphia, PA: Linguistic Data Consortium, University of Pennsylvania
-
- Brady S., Shankweiler D. P. (eds.). (1991). Phonological Process in Literacy. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases