An ortholog of the Leptospira interrogans lipoprotein LipL32 aids in the colonization of Pseudoalteromonas tunicata to host surfaces
- PMID: 25071736
- PMCID: PMC4080168
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00323
An ortholog of the Leptospira interrogans lipoprotein LipL32 aids in the colonization of Pseudoalteromonas tunicata to host surfaces
Abstract
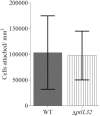
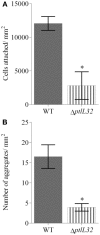
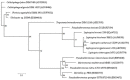
The bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata is a common surface colonizer of marine eukaryotes, including the macroalga Ulva australis.Genomic analysis of P. tunicata identified genes potentially involved in surface colonization, including genes with homology to bacterial virulence factors that mediate attachment. Of particular interest is the presence of a gene, designated ptlL32, encoding an ortholog to the Leptospira lipoprotein LipL32, which has been shown to facilitate the interaction of Leptospira sp. with host extracellular matrix (ECM) structures and is thought to be an important virulence trait for pathogenic Leptospira. To investigate the role of PtlL32 in the colonization by P. tunicata we constructed and characterized a ΔptlL32 mutant strain. Whilst P. tunicata ΔptlL32 bound to an abiotic surface with the same capacity as the wild type strain, it had a marked effect on the ability of P. tunicata to bind to ECM, suggesting a specific role in attachment to biological surfaces. Loss of PtlL32 also significantly reduced the capacity for P. tunciata to colonize the host algal surface demonstrating a clear role for this protein as a host-colonization factor. PtlL32 appears to have a patchy distribution across specific groups of environmental bacteria and phylogenetic analysis of PtlL32 orthologous proteins from non-Leptospira species suggests it may have been acquired via horizontal gene transfer between distantly related lineages. This study provides the first evidence for an attachment function for a LipL32-like protein outside the Leptospira and thereby contributes to the understanding of host colonization in ecologically distinct bacterial species.
Keywords: LipL32; Pseudoalteromonas; algae; bacterial attachment; host-microbe interaction; marine bacteria; seaweed/s.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LipL32 is an extracellular matrix-interacting protein of Leptospira spp. and Pseudoalteromonas tunicata.Infect Immun. 2008 May;76(5):2063-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01643-07. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18285490 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Pseudoalteromonas tunicata genome reveals properties of a surface-associated life style in the marine environment.PLoS One. 2008 Sep 24;3(9):e3252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003252. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18813346 Free PMC article.
-
Low densities of epiphytic bacteria from the marine alga Ulva australis inhibit settlement of fouling organisms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Dec;73(24):7844-52. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01543-07. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17965210 Free PMC article.
-
The lipoprotein LipL32, an enigma of leptospiral biology.Vet Microbiol. 2013 Mar 23;162(2-4):305-314. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23206414 Review.
-
Leptospira spp.: Novel insights into host-pathogen interactions.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016 Aug;176:50-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 26727033 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Dysbiosis: Rethinking Disease in Marine Ecosystems.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 21;7:991. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00991. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27446031 Free PMC article.
-
VarR controls colonization and virulence in the marine macroalgal pathogen Nautella italica R11.Front Microbiol. 2015 Oct 13;6:1130. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01130. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26528274 Free PMC article.
-
The pangenome of (Antarctic) Pseudoalteromonas bacteria: evolutionary and functional insights.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 17;18(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3382-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28095778 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for: Microbial symbiosis of marine sessile hosts- diversity and function.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jun 16;6:585. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00585. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26136729 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Slr4, a newly identified S-layer protein from marine Gammaproteobacteria, is a major biofilm matrix component.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Dec;114(6):979-990. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14588. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32804439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel F. M., Brent R., Kingston R., Moore R., Siedman J., Smith J., et al. (1994). Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

