Salvage radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy: prediction of biochemical outcomes
- PMID: 25072938
- PMCID: PMC4114753
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103574
Salvage radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy: prediction of biochemical outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: A significant proportion of patients undergoing salvage radiotherapy (RT) for biochemical recurrence (BCR) following radical prostatectomy (RP) may again experience BCR after salvage RT. Thus, we evaluated the clinical significances of different parameters on the biochemical outcome of RT in salvage setting.
Methods: We reviewed the records of 212 patients who underwent salvage RT between November 2003 and December 2012 for BCR following primary RP. BCR-free survivals after salvage RT were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to evaluate the impacts of clinicopathologic parameters on BCR following salvage RT.
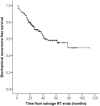
Results: The overall median follow-up duration was 63.5 months. The BCR-free survival rate after salvage RT was 58.2% at 5 years. Multivariate analysis showed that a pre-RT prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level of ≤0.5 ng/mL, a pre-RT PSA doubling time (PSADT) of >4.5 months, concomitant androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) with salvage RT, and a positive surgical margin were independent predictors of favorable biochemical outcomes after salvage RT (hazard ratios [HR] = 3.012, 1.132, 2.000, and 1.805, respectively, p = less than 0.001, 0.013, 0.005, and 0.036, respectively). In the early (pre-RT PSA ≤0.5 ng/mL) salvage RT setting, concomitant ADT administration was also shown to be significantly associated with higher risk of BCR-free survival following salvage RT (HR = 2.611, p = 0.038).
Conclusion: Lower pre-RT PSA value, longer PSADT before salvage RT, concomitant ADT administration, and a positive surgical margin were significant predictors of favorable biochemical outcomes following salvage RT performed for BCR after primary RP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mullins JK, Feng Z, Trock BJ, Epstein JI, Walsh PC, et al. (2012) The impact of anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy on cancer control: the 30-year anniversary. J Urol 188: 2219–2224. - PubMed
-
- Boorjian SA, Eastham JA, Graefen M, Guillonneau B, Karnes RJ, et al. (2012) A critical analysis of the long-term impact of radical prostatectomy on cancer control and function outcomes. Eur Urol 61: 664–675. - PubMed
-
- Pound CR, Partin AW, Eisenberger MA, Chan DW, Pearson JD, et al. (1999) Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA 281: 1591–1597. - PubMed
-
- Hong SK, Park HZ, Lee WK, Kim DS, Lee JS, et al. (2010) Prognostic significance of undetectable ultrasensitive prostate-specific antigen nadir after radical prostatectomy. Urology 76: 723–727. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita H, Shimizu Y, Mizowaki T, Takayama K, Norihisa Y, et al. (2013) Risk factors predicting the outcome of salvage radiotherapy in patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Int J Urol 20: 806–811. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous