Primary implant stability in augmented sinuslift-sites after completed bone regeneration: a randomized controlled clinical study comparing four subantrally inserted biomaterials
- PMID: 25073446
- PMCID: PMC5376201
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05877
Primary implant stability in augmented sinuslift-sites after completed bone regeneration: a randomized controlled clinical study comparing four subantrally inserted biomaterials
Abstract
Implant-Insertion-Torque-Value (ITV) proved to be a significant clinical parameter to predict long term implant success-rates and to decide upon immediate loading. The study evaluated ITVs, when four different and commonly used biomaterials were used in sinuslift-procedures compared to natural subantral bone in two-stage-implant-procedures. The tHUCSL-INTRALIFT-method was chosen for sinuslifting in 155 sinuslift-sites for its minimal invasive transcrestal approach and scalable augmentation volume. Four different biomaterials were inserted randomly (easy-graft CRYSTAL n = 38, easy-graft CLASSIC n = 41, NanoBone n = 42, BioOss n = 34), 2 ccm in each case. After a mean healing period of 8,92 months uniform tapered screw Q2-implants were inserted and Drill-Torque-Values (DTV) and ITV were recorded and compared to a group of 36 subantral sites without need of sinuslifting. DTV/ITV were processed for statistics by ANOVA-tests. Mean DTV/ITV obtained in Ncm were: Control Group 10,2/22,2, Bio-Oss 12,7/26,2, NanoBone 17,5/33,3, easy-graft CLASSIC 20,3/45,9, easy-graft CRYSTAL 23,8/56,6 Ncm, significance-level of differences throughout p < 0,05. Within the limits of this study the results suggest self-hardening solid-block-like bone-graft-materials to achieve significantly better DTV/ITV than loose granulate biomaterials for its suspected improvement of vascularization and mineralization of the subantral scaffold by full immobilization of the augmentation site towards pressure changes in the human sinus at normal breathing.
Conflict of interest statement
The presented study was conducted without any exterior funding as part of routine patient treatment by all authors. Surgery-documentation were not specially altered for the presented study compared to routine patient treatment in the authors' clinics.DrDr Troedhan A, Dr Schlichting I, Dr Kurrek A and Dr Wainwright M declare no conflicts of interests by monetary funding or compensation of their research by Satelec-ACTEON (Piezo-devices), TRINON-Karlsruhe-GmbH (Implant-system), Geistlich (BioOss), ArtOss (NanoBone), SUNSTAR-Degradable (easy-graft), personal funding or dependencies by and from the above mentioned companies or any kind of benefitial remuneration in cash, stocks or stock options or equities.All devices used in this study were regularly purchased from national dental suppliers and are owned by the authors, as well as the used dental-implants and biomaterials as the same implants and biomaterials among other brands are used in the clinical routine of the authors' clinics in all indications for bone-augmentation and implant insertion since 2001 (DrDr Troedhan A, Dr Kurrek A) and 2004 for Dr Schlichting I and Dr Wainwright M.DrDr Troedhan A, Dr Kurrek A and Dr Wainwright M - forming the independent “TKW-Research-Group” - hold a non-remunerated co-inventorship on the patent filed for the ultrasonic surgical tool-tips for the Intralift-sinuslift and are supported by Satelec-ACTEON in prototyping and manufacturing new Piezotome-applicator-tips designed by these three authors since Satelec-ACTEON discloses revelation of exact specifications on metal/resin-alloys and oscillation-induction for their ultrasonic surgical devices. In case of invitations of DrDr Troedhan A, Dr Schlichting I, Dr Kurrek A and Dr Wainwright M by Universities, educational institutions or organizers of hands-on workshops for qualified dentists' training in cooperation with one of the above mentioned companies, travel-expenses, accommodation and daily diets, regulated by Austrian and German law, are remunerated.Dr Kurrek A was a non-remunerated chief-medical advisor in the development of the Q-implant-system from 1997–1999 and Dr Kurrek A and Dr Troedhan A lead international implantology-courses as visiting Professors at the Health Science University Vientiane/Laos, Faculty of Dentistry in cooperation with TRINON GmbH.
Figures
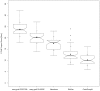
 ] represent the outliers. Within the boxes the notches mark the confidence interval based on the median +/− 1.58 (IQR/sqrt of n) [n = number of measurements]. Additionally, the mean value is indicated by a black square [
] represent the outliers. Within the boxes the notches mark the confidence interval based on the median +/− 1.58 (IQR/sqrt of n) [n = number of measurements]. Additionally, the mean value is indicated by a black square [ ] and the cross symbol [+] displays the standard deviation. Bio-Oss (n = 34), NanoBone (n = 42), easy-graft CLASSIC (n = 41), easy-graft CRYSTAL (n = 38), Control Group (n = 36).
] and the cross symbol [+] displays the standard deviation. Bio-Oss (n = 34), NanoBone (n = 42), easy-graft CLASSIC (n = 41), easy-graft CRYSTAL (n = 38), Control Group (n = 36).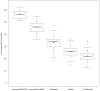
 ] represent the outliers. Within the boxes the notches mark the confidence interval based on the median +/− 1.58 (IQR/sqrt of n) [n = number of measurements]. Additionally, the mean value is indicated by a black square [
] represent the outliers. Within the boxes the notches mark the confidence interval based on the median +/− 1.58 (IQR/sqrt of n) [n = number of measurements]. Additionally, the mean value is indicated by a black square [ ] and the cross symbol [+] displays the standard deviation. Bio-Oss (n = 34), NanoBone (n = 42), easy-graft CLASSIC (n = 41), easy-graft CRYSTAL (n = 38), Control Group (n = 36).
] and the cross symbol [+] displays the standard deviation. Bio-Oss (n = 34), NanoBone (n = 42), easy-graft CLASSIC (n = 41), easy-graft CRYSTAL (n = 38), Control Group (n = 36).Similar articles
-
Do Clinical and Radiological Assessments Contribute to the Understanding of Biomaterials? Results From a Prospective Randomized Sinus Augmentation Split-Mouth Trial.J Oral Implantol. 2018 Feb;44(1):62-69. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-17-00139. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Oral Implantol. 2018. PMID: 29091020 Clinical Trial.
-
Early implant loading in the atrophic posterior maxilla: 1-stage lateral versus crestal sinus lift and 8 mm hydroxyapatite-coated implants. A 5-year randomised controlled trial.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2013 Spring;6(1):13-25. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2013. PMID: 23513199 Clinical Trial.
-
Insertion Torque of Variable-Thread Tapered Implants in the Posterior Maxilla: A Clinical Study.J Prosthodont. 2019 Feb;28(2):e788-e794. doi: 10.1111/jopr.12965. Epub 2018 Sep 4. J Prosthodont. 2019. PMID: 30178903
-
Reconstruction of the severely resorbed maxilla with dental implants in the augmented maxillary sinus: a 5-year clinical investigation.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996 Jul-Aug;11(4):466-75. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996. PMID: 8803342
-
Bone formation with a biphasic calcium phosphate combined with fibrin sealant in maxillary sinus floor elevation for delayed dental implant.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Sep;23(9):1112-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02275.x. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. PMID: 22892064 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Minimally Invasive Alveolar Ridge Preservation Utilizing an In Situ Hardening β-Tricalcium Phosphate Bone Substitute: A Multicenter Case Series.Int J Dent. 2016;2016:5406736. doi: 10.1155/2016/5406736. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Int J Dent. 2016. PMID: 27190516 Free PMC article.
-
The use of hydroxyapatite bone substitute grafting for alveolar ridge preservation, sinus augmentation, and periodontal bone defect: A systematic review.Heliyon. 2018 Nov 2;4(10):e00884. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00884. eCollection 2018 Oct. Heliyon. 2018. PMID: 30417149 Free PMC article.
-
Ridge preservation using an in situ hardening biphasic calcium phosphate (β-TCP/HA) bone graft substitute-a clinical, radiological, and histological study.Int J Implant Dent. 2017 Dec;3(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40729-017-0086-2. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Int J Implant Dent. 2017. PMID: 28643222 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Healing in Rabbit Calvaria Defects Using a Synthetic Bone Substitute: A Histological and Micro-CT Comparative Study.Materials (Basel). 2018 Oct 17;11(10):2004. doi: 10.3390/ma11102004. Materials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30336544 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Periodontal Gap After Long-Term Tooth Movement into Augmented Critical-Sized Defects in the Jaws of Beagle Dogs.Dent J (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;12(12):386. doi: 10.3390/dj12120386. Dent J (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39727443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friberg B., Sennerby L., Roos J. & Lekholm U. Identification of bone quality in conjunction with insertion of titanium implants. A pilot study in jaw autopsy specimens. Clin Oral Impl Res. 6, 213–219 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Alsaadi G., Quirynen M., Michiels K., Jacobs R. & Van Steenberghe D. A biomechanical assessment of the relation between the oral implant stability at insertion and subjective bone quality assessment. J. Clin Periodontol. 34, 359–366 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Turkyilmaz I., Tözüm T. F., Tumer C. & Ozbek E. N. Assessment of correlation between computerized tomography values of the bone, and maximum torque and resonance frequency values at dental implant placement. J. Oral Rehab. 33, 881–888 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Turkyilmaz I., Tumer C., Ozbek E. N. & Tözüm T. F. Relations between the bone density values from computerized tomography, and implant stability parameters: a clinical study of 230 regular platform implants. J. Clin Periodontol. 34, 716–722 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Turkyilmaz I., Aksoy U. & McGlumphy E. A. Two alternative surgical techniques for enhancing primary implant stability in the posterior maxilla: a clinical study including bone density, insertion torque, and resonance frequency analysis data. Clin Impl Dent Rel Res. 10, 231–237 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

