Bile acid signaling in metabolic disease and drug therapy
- PMID: 25073467
- PMCID: PMC4180336
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.113.008201
Bile acid signaling in metabolic disease and drug therapy
Abstract
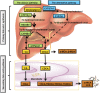
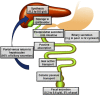
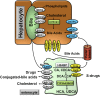
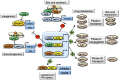
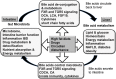
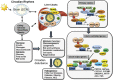
Bile acids are the end products of cholesterol catabolism. Hepatic bile acid synthesis accounts for a major fraction of daily cholesterol turnover in humans. Biliary secretion of bile acids generates bile flow and facilitates hepatobiliary secretion of lipids, lipophilic metabolites, and xenobiotics. In the intestine, bile acids are essential for the absorption, transport, and metabolism of dietary fats and lipid-soluble vitamins. Extensive research in the last 2 decades has unveiled new functions of bile acids as signaling molecules and metabolic integrators. The bile acid-activated nuclear receptors farnesoid X receptor, pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, vitamin D receptor, and G protein-coupled bile acid receptor play critical roles in the regulation of lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism, inflammation, and drug metabolism and detoxification. Bile acid synthesis exhibits a strong diurnal rhythm, which is entrained by fasting and refeeding as well as nutrient status and plays an important role for maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Recent research revealed an interaction of liver bile acids and gut microbiota in the regulation of liver metabolism. Circadian disturbance and altered gut microbiota contribute to the pathogenesis of liver diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes, and obesity. Bile acids and their derivatives are potential therapeutic agents for treating metabolic diseases of the liver.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures




References
-
- Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabès JP, Allard D, Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich D, et al. (2003) Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat Genet 34:154–156 - PubMed
-
- Adorini L, Pruzanski M, Shapiro D. (2012) Farnesoid X receptor targeting to treat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Drug Discov Today 17:988–997 - PubMed
-
- Aldridge MA, Ito MK. (2001) Colesevelam hydrochloride: a novel bile acid-binding resin. Ann Pharmacother 35:898–907 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

