Origin of myofibroblasts in the fibrotic liver in mice
- PMID: 25074909
- PMCID: PMC4136601
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1400062111
Origin of myofibroblasts in the fibrotic liver in mice
Abstract
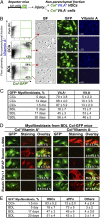
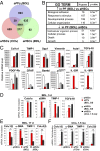
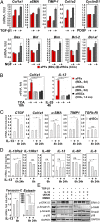
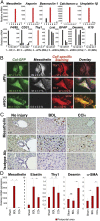
Hepatic myofibroblasts are activated in response to chronic liver injury of any etiology to produce a fibrous scar. Despite extensive studies, the origin of myofibroblasts in different types of fibrotic liver diseases is unresolved. To identify distinct populations of myofibroblasts and quantify their contribution to hepatic fibrosis of two different etiologies, collagen-α1(I)-GFP mice were subjected to hepatotoxic (carbon tetrachloride; CCl4) or cholestatic (bile duct ligation; BDL) liver injury. All myofibroblasts were purified by flow cytometry of GFP(+) cells and then different subsets identified by phenotyping. Liver resident activated hepatic stellate cells (aHSCs) and activated portal fibroblasts (aPFs) are the major source (>95%) of fibrogenic myofibroblasts in these models of liver fibrosis in mice. As previously reported using other methodologies, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the major source of myofibroblasts (>87%) in CCl4 liver injury. However, aPFs are a major source of myofibroblasts in cholestatic liver injury, contributing >70% of myofibroblasts at the onset of injury (5 d BDL). The relative contribution of aPFs decreases with progressive injury, as HSCs become activated and contribute to the myofibroblast population (14 and 20 d BDL). Unlike aHSCs, aPFs respond to stimulation with taurocholic acid and IL-25 by induction of collagen-α1(I) and IL-13, respectively. Furthermore, BDL-activated PFs express high levels of collagen type I and provide stimulatory signals to HSCs. Gene expression analysis identified several novel markers of aPFs, including a mesothelial-specific marker mesothelin. PFs may play a critical role in the pathogenesis of cholestatic liver fibrosis and, therefore, serve as an attractive target for antifibrotic therapy.
Keywords: ECM deposition; markers of fibrogenic myofibroblasts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM41804/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72237/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK088837/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AA15055/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099205/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072237/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI0777802/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK088837/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA015055/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041804/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

