Coronavirus Nsp10, a critical co-factor for activation of multiple replicative enzymes
- PMID: 25074927
- PMCID: PMC4162180
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.577353
Coronavirus Nsp10, a critical co-factor for activation of multiple replicative enzymes
Abstract
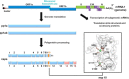
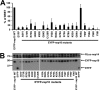
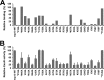
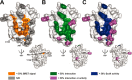
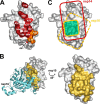
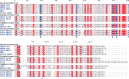
The RNA-synthesizing machinery of the severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is composed of 16 non-structural proteins (nsp1-16) encoded by ORF1a/1b. The 148-amino acid nsp10 subunit contains two zinc fingers and is known to interact with both nsp14 and nsp16, stimulating their respective 3'-5' exoribonuclease and 2'-O-methyltransferase activities. Using alanine-scanning mutagenesis, in cellulo bioluminescence resonance energy transfer experiments, and in vitro pulldown assays, we have now identified the key residues on the nsp10 surface that interact with nsp14. The functional consequences of mutations introduced at these positions were first evaluated biochemically by monitoring nsp14 exoribonuclease activity. Disruption of the nsp10-nsp14 interaction abrogated the nsp10-driven activation of the nsp14 exoribonuclease. We further showed that the nsp10 surface interacting with nsp14 overlaps with the surface involved in the nsp10-mediated activation of nsp16 2'-O-methyltransferase activity, suggesting that nsp10 is a major regulator of SARS-CoV replicase function. In line with this notion, reverse genetics experiments supported an essential role of the nsp10 surface that interacts with nsp14 in SARS-CoV replication, as several mutations that abolished the interaction in vitro yielded a replication-negative viral phenotype. In contrast, mutants in which the nsp10-nsp16 interaction was disturbed proved to be crippled but viable. These experiments imply that the nsp10 surface that interacts with nsp14 and nsp16 and possibly other subunits of the viral replication complex may be a target for the development of antiviral compounds against pathogenic coronaviruses.
Keywords: Genetics; Protein-Protein Interaction; RNA Methyltransferase; RNA Virus; Viral Replication; Viral Transcription.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Nga P. T., Parquet Mdel C., Lauber C., Parida M., Nabeshima T., Yu F., Thuy N. T., Inoue S., Ito T., Okamoto K., Ichinose A., Snijder E. J., Morita K., Gorbalenya A. E. (2011) Discovery of the first insect Nidovirus, a missing evolutionary link in the emergence of the largest RNA virus genomes. PLoS Pathog. 7, e1002215. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

