Adropin is a brain membrane-bound protein regulating physical activity via the NB-3/Notch signaling pathway in mice
- PMID: 25074942
- PMCID: PMC4162195
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.576058
Adropin is a brain membrane-bound protein regulating physical activity via the NB-3/Notch signaling pathway in mice
Abstract
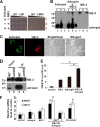
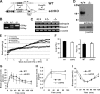
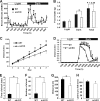
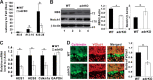
Adropin is a highly conserved polypeptide that has been suggested to act as an endocrine factor that plays important roles in metabolic regulation, insulin sensitivity, and endothelial functions. However, in this study, we provide evidence demonstrating that adropin is a plasma membrane protein expressed abundantly in the brain. Using a yeast two-hybrid screening approach, we identified NB-3/Contactin 6, a brain-specific, non-canonical, membrane-tethered Notch1 ligand, as an interaction partner of adropin. Furthermore, this interaction promotes NB3-induced activation of Notch signaling and the expression of Notch target genes. We also generated and characterized adropin knockout mice to explore the role of adropin in vivo. Adropin knockout mice exhibited decreased locomotor activity and impaired motor coordination coupled with defective synapse formation, a phenotype similar to NB-3 knockout mice. Taken together, our data suggest that adropin is a membrane-bound protein that interacts with the brain-specific Notch1 ligand NB3. It regulates physical activity and motor coordination via the NB-3/Notch signaling pathway and plays an important role in cerebellum development in mice.
Keywords: Adropin; Energy Metabolism; Locomotor Activity Motor Coordination; Membrane Protein; Molecular Cell Biology; NB-3; Notch Pathway; Yeast Two-hybrid.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Kumar K. G., Trevaskis J. L., Lam D. D., Sutton G. M., Koza R. A., Chouljenko V. N., Kousoulas K. G., Rogers P. M., Kesterson R. A., Thearle M., Ferrante A. W., Jr., Mynatt R. L., Burris T. P., Dong J. Z., Halem H. A., Culler M. D., Heisler L. K., Stephens J. M., Butler A. A. (2008) Identification of adropin as a secreted factor linking dietary macronutrient intake with energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Cell Metab. 8, 468–481 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lovren F., Pan Y., Quan A., Singh K. K., Shukla P. C., Gupta M., Al-Omran M., Teoh H., Verma S. (2010) Adropin is a novel regulator of endothelial function. Circulation 122, S185–S192 - PubMed
-
- Aydin S., Kuloglu T., Aydin S. (2013) Copeptin, adropin and irisin concentrations in breast milk and plasma of healthy women and those with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 47, 66–70 - PubMed
-
- Butler A. A., Tam C. S., Stanhope K. L., Wolfe B. M., Ali M. R., O'Keeffe M., St-Onge M. P., Ravussin E., Havel P. J. (2012) Low circulating adropin concentrations with obesity and aging correlate with risk factors for metabolic disease and increase after gastric bypass surgery in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, 3783–3791 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

