Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments
- PMID: 25075198
- PMCID: PMC4106026
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S65979
Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments
Abstract
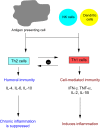
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is defined as a chronic intestinal inflammation that results from host-microbial interactions in a genetically susceptible individual. IBDs are a group of autoimmune diseases that are characterized by inflammation of both the small and large intestine, in which elements of the digestive system are attacked by the body's own immune system. This inflammatory condition encompasses two major forms, known as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Patients affected by these diseases experience abdominal symptoms, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloody stools, and vomiting. Moreover, defects in intestinal epithelial barrier function have been observed in a number of patients affected by IBD. In this review, we first describe the types and symptoms of IBD and investigate the role that the epithelial barrier plays in the pathophysiology of IBD as well as the major cytokines involved. We then discuss steps used to diagnose this disease and the treatment options available, and finally provide an overview of the recent research that aims to develop new therapies for such chronic disorders.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; cytokines; inflammatory bowel disease; ulcerative colitis.
Figures


References
-
- Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature. 2001;411:603–606. - PubMed
-
- Shoda R, Matsueda K, Yamato S, Umeda N. Epidemiologic analysis of Crohn disease in Japan: increased dietary intake of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and animal protein relates to the increased incidence of Crohn disease in Japan. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;64:741–745. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

