Divergent effects of first-generation and second-generation antipsychotics on cortical thickness in first-episode psychosis
- PMID: 25077698
- PMCID: PMC4413868
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291714001652
Divergent effects of first-generation and second-generation antipsychotics on cortical thickness in first-episode psychosis
Abstract
Background: Whether there are differential effects of first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) on the brain is currently debated. Although some studies report that FGAs reduce grey matter more than SGAs, others do not, and research to date is limited by a focus on schizophrenia spectrum disorders. To address this limitation, this study investigated the effects of medication in patients being treated for first-episode schizophrenia or affective psychoses.
Method: Cortical thickness was compared between 52 first-episode psychosis patients separated into diagnostic (i.e. schizophrenia or affective psychosis) and medication (i.e. FGA and SGA) subgroups. Patients in each group were also compared to age- and sex-matched healthy controls (n = 28). A whole-brain cortical thickness interaction analysis of medication and diagnosis was then performed. Correlations between cortical thickness with antipsychotic dose and psychotic symptoms were examined.
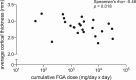
Results: The effects of medication and diagnosis did not interact, suggesting independent effects. Compared with controls, diagnostic differences were found in frontal, parietal and temporal regions. Decreased thickness in FGA-treated versus SGA-treated groups was found in a large frontoparietal region (p < 0.001, corrected). Comparisons with healthy controls revealed decreased cortical thickness in the FGA group whereas the SGA group showed increases in addition to decreases. In FGA-treated patients cortical thinning was associated with higher negative symptoms whereas increased cortical thickness in the SGA-treated group was associated with lower positive symptoms.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that FGA and SGA treatments have divergent effects on cortical thickness during the first episode of psychosis that are independent from changes due to illness.
Keywords: Antipsychotics; cortical thickness; first-episode psychosis; first-generation; second-generation.
Figures


References
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M (2005). Mechanisms of action of second generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: insights from brain imaging studies. European Psychiatry 20, 15–27. - PubMed
-
- Aguado F, Carmona MA, Pozas E, Aguiló A, Martínez-Guijarro FJ, Alcantara S, Borrell V, Yuste R, Ibañez CF, Soriano E (2003). BDNF regulates spontaneous correlated activity at early developmental stages by increasing synaptogenesis and expression of the K+/Cl- co-transporter KCC2. Development 130, 1267–1280. - PubMed
-
- Bora E, Fornito A, Yücel M, Pantelis C (2010). Voxelwise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in bipolar disorder. Biological Psychiatry 67, 1097–1105. - PubMed
-
- Boter H, Peuskens J, Libiger J, Fleischhacker WW, Davidson M, Galderisi S, Kahn RS; EUFEST study group (2009). Effectiveness of antipsychotics in first-episode schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder on response and remission: an open randomized clinical trial (EUFEST). Schizophrenia Research 115, 97–103. - PubMed
-
- Cahn W, van Haren NEM, Hulshoff Pol HE, Schnack HG, Caspers E, Laponder DAJ, Kahn RS (2006). Brain volume changes in the first year of illness and 5-year outcome of schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 189, 381–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

