Distribution and medical impact of loss-of-function variants in the Finnish founder population
- PMID: 25078778
- PMCID: PMC4117444
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004494
Distribution and medical impact of loss-of-function variants in the Finnish founder population
Abstract
Exome sequencing studies in complex diseases are challenged by the allelic heterogeneity, large number and modest effect sizes of associated variants on disease risk and the presence of large numbers of neutral variants, even in phenotypically relevant genes. Isolated populations with recent bottlenecks offer advantages for studying rare variants in complex diseases as they have deleterious variants that are present at higher frequencies as well as a substantial reduction in rare neutral variation. To explore the potential of the Finnish founder population for studying low-frequency (0.5-5%) variants in complex diseases, we compared exome sequence data on 3,000 Finns to the same number of non-Finnish Europeans and discovered that, despite having fewer variable sites overall, the average Finn has more low-frequency loss-of-function variants and complete gene knockouts. We then used several well-characterized Finnish population cohorts to study the phenotypic effects of 83 enriched loss-of-function variants across 60 phenotypes in 36,262 Finns. Using a deep set of quantitative traits collected on these cohorts, we show 5 associations (p<5×10⁻⁸) including splice variants in LPA that lowered plasma lipoprotein(a) levels (P = 1.5×10⁻¹¹⁷). Through accessing the national medical records of these participants, we evaluate the LPA finding via Mendelian randomization and confirm that these splice variants confer protection from cardiovascular disease (OR = 0.84, P = 3×10⁻⁴), demonstrating for the first time the correlation between very low levels of LPA in humans with potential therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases. More generally, this study articulates substantial advantages for studying the role of rare variation in complex phenotypes in founder populations like the Finns and by combining a unique population genetic history with data from large population cohorts and centralized research access to National Health Registers.
Conflict of interest statement
Abbott Diagnostics provided test reagents for FINRISK 1997 determinations of Galectin-3, Lp(a) and D-dimer within the framework of the MORGAM Biomarker Study and the BiomarCaRE project. SBl has received honoraria from Abbott Diagnostics, SIEMENS, Thermo Fisher and Roche Diagnostics and is a consultant for Thermo Fisher. VS has received a speaker honorarium from Roche Diagnostics. All other co-authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Figures
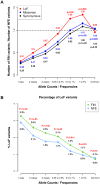
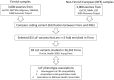

Comment in
-
Population genomics: a new window into the genetics of complex diseases.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Oct;15(10):644-5. doi: 10.1038/nrg3815. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25139190 No abstract available.
References
-
- Styrkarsdottir U, Thorleifsson G, Sulem P, Gudbjartsson DF, Sigurdsson A, et al. (2013) Nonsense mutation in the LGR4 gene is associated with several human diseases and other traits. Nature 497: 517–520. - PubMed
-
- Jonsson T, Atwal JK, Steinberg S, Snaedal J, Jonsson PV, et al. (2012) A mutation in APP protects against Alzheimer's disease and age-related cognitive decline. Nature 488: 96–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 086596/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01-DK-085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090367/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RC2 DK088389/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RFA-HL-12-007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK085584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113315/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL-102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2-DK088389/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

