Novel approach identifies SNPs in SLC2A10 and KCNK9 with evidence for parent-of-origin effect on body mass index
- PMID: 25078964
- PMCID: PMC4117451
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004508
Novel approach identifies SNPs in SLC2A10 and KCNK9 with evidence for parent-of-origin effect on body mass index
Abstract
The phenotypic effect of some single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) depends on their parental origin. We present a novel approach to detect parent-of-origin effects (POEs) in genome-wide genotype data of unrelated individuals. The method exploits increased phenotypic variance in the heterozygous genotype group relative to the homozygous groups. We applied the method to >56,000 unrelated individuals to search for POEs influencing body mass index (BMI). Six lead SNPs were carried forward for replication in five family-based studies (of ∼4,000 trios). Two SNPs replicated: the paternal rs2471083-C allele (located near the imprinted KCNK9 gene) and the paternal rs3091869-T allele (located near the SLC2A10 gene) increased BMI equally (beta = 0.11 (SD), P<0.0027) compared to the respective maternal alleles. Real-time PCR experiments of lymphoblastoid cell lines from the CEPH families showed that expression of both genes was dependent on parental origin of the SNPs alleles (P<0.01). Our scheme opens new opportunities to exploit GWAS data of unrelated individuals to identify POEs and demonstrates that they play an important role in adult obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Dauvilliers has received speaker's honoraria and support for travel to meetings from UCB Pharma, JAZZ and Bioprojet. Prof. Dauvilliers participated in advisory boards of UCB Pharma, JAZZ and Bioprojet. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
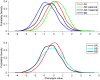
 ). Therefore the average phenotype in the B/B group is the same as in the A/A group, as the paternal and maternal B allele effects cancel each other out. In the A/B group there are two subpopulations: the A-pat/B-mat group with phenotypic mean of
). Therefore the average phenotype in the B/B group is the same as in the A/A group, as the paternal and maternal B allele effects cancel each other out. In the A/B group there are two subpopulations: the A-pat/B-mat group with phenotypic mean of  and the A-mat/B-pat group with
and the A-mat/B-pat group with  mean. Thus, the two subpopulations combined also have zero mean, but increased variance.
mean. Thus, the two subpopulations combined also have zero mean, but increased variance.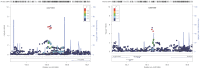
References
-
- Guilmatre A, Sharp AJ (2012) Parent of origin effects. Clin Genet 81: 201–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AA007535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA014041/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AA014041/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 084723/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- AA13326/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G0601966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0100266/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH063706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RP-PG-0310-1002/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- R01HL59367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G1002319/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AA13320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 0927310/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01DK8925601/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DA12854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA13321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA10248/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 0927310/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 5R01MH63706:02/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL091823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013326/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RL1MH083268-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_0801/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268200625226C/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 102215/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 097117/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZD/16/6/4/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/09/012/28096/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL087679-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- RL1 MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA07535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- WT083431MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T32 HL007055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AA013320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

