Analysis of nuclear RNA interference in human cells by subcellular fractionation and Argonaute loading
- PMID: 25079428
- PMCID: PMC4251768
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2014.135
Analysis of nuclear RNA interference in human cells by subcellular fractionation and Argonaute loading
Abstract
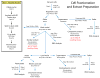
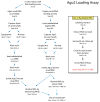
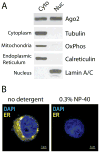
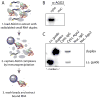
RNAi is well known for its ability to regulate gene expression in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells. In mammalian cell nuclei, however, the impact of RNAi has remained more controversial. A key technical hurdle has been a lack of optimized protocols for the isolation and analysis of cell nuclei. Here we describe a simplified protocol for nuclei isolation from cultured cells that incorporates a method for obtaining nucleoplasmic and chromatin fractions and removing cytoplasmic contamination. Cell fractions can then be used to detect the presence and activity of RNAi factors in the nucleus. We include a method for investigating an early step in RNAi, Argonaute protein loading with small RNAs, which is enabled by our improved extract preparations. This protocol facilitates the characterization of nuclear RNAi, and it can be applied to the analysis of other nuclear proteins and pathways. From cellular fractionation to analysis of Argonaute loading results, this protocol takes 4-6 d to complete.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Janowski BA, et al. Inhibiting gene expression at transcription start sites in chromosomal DNA with antigen RNAs. Nat Chem Bio. 2005;1:216–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

