IND-directed safety and biodistribution study of intravenously injected cetuximab-IRDye800 in cynomolgus macaques
- PMID: 25080323
- PMCID: PMC4318248
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-014-0773-9
IND-directed safety and biodistribution study of intravenously injected cetuximab-IRDye800 in cynomolgus macaques
Abstract
Purpose: The use of receptor-targeted antibodies conjugated to fluorophores is actively being explored for real-time imaging of disease states; however, the toxicity of the bioconjugate has not been assessed in non-human primates.
Procedures: To this end, the in vivo toxicity and pharmacokinetics of IRDye800 conjugated to cetuximab (cetuximab-IRDye800; 21 mg/kg; equivalent to 250 mg/m(2) human dose) were assessed in male cynomolgus monkeys over 15 days following intravenous injection and compared with an unlabeled cetuximab-dosed control group.
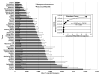
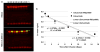
Results: Cetuximab-IRDye800 was well tolerated. There were no infusion reactions, adverse clinical signs, mortality, weight loss, or clinical histopathology findings. The plasma half-life for the cetuximab-IRDye800 and cetuximab groups was equivalent (2.5 days). The total recovered cetuximab-IRDye800 in all tissues at study termination was estimated to be 12 % of the total dose. Both cetuximab-IRDye800 and cetuximab groups showed increased QTc after dosing. The QTc for the cetuximab-dosed group returned to baseline by day 15, while the QTc of the cetuximab-IRDye800 remained elevated compared to baseline.
Conclusion: IRDye800 in low molar ratios does not significantly impact cetuximab half-life or result in organ toxicity. These studies support careful cardiac monitoring (ECG) for human studies using fluorescent dyes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rosenthal EL, Kulbersh BD, Duncan RD, et al. In vivo detection of head and neck cancer orthotopic xenografts by immunofluorescence. Laryngoscope. 2006;116:1636–1641. - PubMed
-
- Gleysteen JP, Duncan RD, Magnuson JS, Skipper JB, Zinn K, Rosenthal EL. Fluorescently labeled cetuximab to evaluate head and neck cancer response to treatment. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6:1181–1185. - PubMed
-
- Kulbersh BD, Duncan RD, Magnuson JS, Skipper JB, Zinn K, Rosenthal EL. Sensitivity and specificity of fluorescent immunoguided neoplasm detection in head and neck cancer xenografts. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133:511–515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

