A pilot randomized controlled trial of a behavioral family-based intervention with and without home visits to decrease obesity in preschoolers
- PMID: 25080605
- PMCID: PMC4166702
- DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsu059
A pilot randomized controlled trial of a behavioral family-based intervention with and without home visits to decrease obesity in preschoolers
Abstract
Objective: Tested two family-based behavioral treatments for obesity in preschool children, one meeting the Expert Committee guidelines for Stage 3 obesity intervention criteria (LAUNCH-clinic) and one exceeding Stage 3 (LAUNCH with home visit [LAUNCH-HV]), compared with a Stage 1 intervention, pediatrician counseling (PC).
Methods: In all, 42 children aged 2-5 years with a body mass index (BMI) percentile of ≥95th were randomized. A total of 33 met intent-to-treat criteria. Assessments were conducted at baseline, Month 6 (posttreatment), and Month 12 (6-month follow-up).
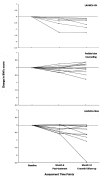
Results: LAUNCH-HV demonstrated a significantly greater decrease on the primary outcome of change in BMI z-score (BMIz) pre- to posttreatment compared with PC (p = .007), whereas LAUNCH-clinic was not significantly different from PC (p = .08). Similar results were found for secondary outcomes.
Conclusions: LAUNCH-HV, but not LAUNCH-clinic, significantly reduced BMIz compared with PC by posttreatment, indicating the need for intensive behavioral intervention, including home visitation, to address weight management in obese preschool children.
Keywords: home visits; obesity; preschoolers; treatment.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Pediatric Psychology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Addessi E, Galloway A T, Visalberghi E, Birch L L. Specific social influences on the acceptance of novel foods in 2-5-year-old children. Appetite. 2005;45:264–271. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2005.07.007. - PubMed
-
- Agras W S, Hammer L D, McNicholas F, Kraemer H C. Risk factors for childhood overweight: A prospective study from birth to 9.5 years. Journal of Pediatrics. 2004;145:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Barlow S E. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: Summary report. Pediatrics. 2007;120(Suppl. 4):S164–S192. doi:120/Supplement_4/S164 [pii] 10.1542/peds.2007-2329C. - PubMed
-
- Birch L L, Fisher J O, Grimm-Thomas K, Markey C N, Sawyer R, Johnson S L. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Child Feeding Questionnaire: A measure of parental attitudes, beliefs and practices about child feeding and obesity proneness. Appetite. 2001;36:201–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

