Common and unique features of viral RNA-dependent polymerases
- PMID: 25080879
- PMCID: PMC4207942
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1695-z
Common and unique features of viral RNA-dependent polymerases
Abstract
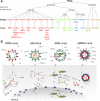
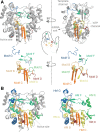
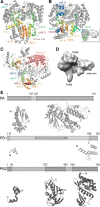
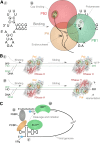
Eukaryotes and bacteria can be infected with a wide variety of RNA viruses. On average, these pathogens share little sequence similarity and use different replication and transcription strategies. Nevertheless, the members of nearly all RNA virus families depend on the activity of a virally encoded RNA-dependent polymerase for the condensation of nucleotide triphosphates. This review provides an overview of our current understanding of the viral RNA-dependent polymerase structure and the biochemistry and biophysics that is involved in replicating and transcribing the genetic material of RNA viruses.
Figures





References
-
- Butel JS. Viral carcinogenesis: revelation of molecular mechanisms and etiology of human disease. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:405–426. - PubMed
-
- Fraaij PL, Bodewes R, Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF. The ins and outs of universal childhood influenza vaccination. Future Microbiol. 2011;6:1171–1184. - PubMed
-
- Patel MM, Glass R, Desai R, Tate JE, Parashar UD. Fulfilling the promise of rotavirus vaccines: how far have we come since licensure? Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:561–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

