Emerging roles for hyaluronidase in cancer metastasis and therapy
- PMID: 25081524
- PMCID: PMC4445717
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800092-2.00001-0
Emerging roles for hyaluronidase in cancer metastasis and therapy
Abstract
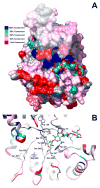
Hyaluronidases are a family of five human enzymes that have been differentially implicated in the progression of many solid tumor types, both clinically and in functional studies. Advances in the past 5 years have clarified many apparent contradictions: (1) by demonstrating that specific hyaluronidases have alternative substrates to hyaluronan (HA) or do not exhibit any enzymatic activity, (2) that high-molecular weight HA polymers elicit signaling effects that are opposite those of the hyaluronidase-digested HA oligomers, and (3) that it is actually the combined overexpression of HA synthesizing enzymes with hyaluronidases that confers tumorigenic potential. This review examines the literature supporting these conclusions and discusses novel mechanisms by which hyaluronidases impact invasive tumor cell processes. In addition, a detailed structural and functional comparison of the hyaluronidases is presented with insights into substrate selectivity and potential for therapeutic targeting. Finally, technological advances in targeting hyaluronidase for tumor imaging and cancer therapy are summarized.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Hyaluronan; Hyaluronidase; Metastasis; Tumor biology; Tumor imaging.
© 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
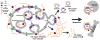
References
-
- Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Tammi R, Tammi M, Viitanen J, Kankkunen JP, et al. Strong Stromal Hyaluronan Expression Is Associated with PSA Recurrence in Local Prostate Cancer. Urol Int. 2002;69:266–272. - PubMed
-
- Andre B, Duterme C, Van Moer K, Mertens-Strijthagen J, Jadot M, Flamion B. Hyal2 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored, lipid raft-associated hyaluronidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;411:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990;61:1303–1313. - PubMed
-
- Atmuri V, Martin DC, Hemming R, Gutsol A, Byers S, Sahebjam S, et al. Hyaluronidase 3 (HYAL3) knockout mice do not display evidence of hyaluronan accumulation. Matrix Biol. 2008;27:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Beech DJ, Madan AK, Deng N. Expression of PH-20 in normal and neoplastic breast tissue. J Surg Res. 2002;103:203–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

