Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes oncogenic signaling, microRNA functions, chemoresistance, and radiation resistance in cancer stem cells leading to tumor progression
- PMID: 25081533
- PMCID: PMC6759082
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800092-2.00010-1
Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes oncogenic signaling, microRNA functions, chemoresistance, and radiation resistance in cancer stem cells leading to tumor progression
Abstract
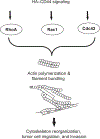
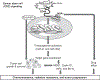
Hyaluronan (HA), a major component of the extracellular matrix (ECM), is enriched in many types of tumors. There is good evidence linking high levels of HA production in human carcinomas to an aggressive phenotype and tumor metastasis. HA is generally bound to CD44 isoforms (so-called CD44s and CD44v3) which are ubiquitous, abundant, and functionally important cell surface receptors. This chapter describes the evidence for HA/CD44v3-mediated activation of the cytoskeleton (e.g., ankyrin and GTPases) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) signaling during tumor progression. A special focus is placed on the role of HA-CD44v3 interaction in cancer stem cells (CSCs). Matrix HA is known to be present in CSC niches. Since CD44v3 serves as a CSC marker, it provides an important physical linkage between matrix HA and various transcription factors that regulate tumor cell functions through distinct signaling pathways. CSCs are known to be chemoresistant and/or radiation resistant and to cause cancer relapse. The purpose of this chapter is to review the most current research on the cellular and molecular biology of CSCs. The emphasis will be placed on both CSC niche and matrix HA-induced microRNA signaling plus various CSC functions (e.g., self-renewal, differentiation, and chemoresistance) during cancer progression. Understanding the regulation of CSCs is critically important for designing CSC-specific therapeutic targets to prevent cancer development and progression.
Keywords: CD44; Cancer stem cells; Chemoresistance; Matrix hyaluronan; Radiation resistance; Tumor progression; microRNAs.
© 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene, 27, 2128–2136. - PubMed
-
- Astachov L, Vago R, Aviv M, & Nevo Z (2011). Hyaluronan and mesenchymal stem cells: From germ layer to cartilage and bone. Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark Edition), 16, 261–276. - PubMed
-
- Auvinen P, Tammi R, Tammi M, Johansson R, & Kosma VM (2005). Expression of CD44s, CD44v3 and CD44v6 in benign and malignant breast lesions: Correlation and colocalization with hyaluronan. Histopathology, 47, 420–428. - PubMed
-
- Baker EK, & El-Osta A (2004). MDR1, chemotherapy and chromatin remodeling. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 3, 819–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

