Routine use of thiopurines in maintaining remission in pediatric Crohn's disease
- PMID: 25083093
- PMCID: PMC4112859
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9185
Routine use of thiopurines in maintaining remission in pediatric Crohn's disease
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness of thiopurines in maintaining steroid-free remission in routine clinical practice.
Methods: The multi-center Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Network (PIBDNet) cohort study prospectively collected data on thiopurine naïve patients initiating mercaptopurine (6MP) or azathioprine. Patients with a diagnosis of Crohn's disease (CD) were included in our study upon entering remission as determined by physician global assessment (PGA) within 365 d of initiation of thiopurines. The primary outcome of the study was maintenance of steroid-free remission (SFR) at each follow up visit. Patients were considered treatment failures if there had been a change in PGA from remission to mild, moderate or severe disease; disease relapse between visits; need for rescue therapy (biologic therapy, methotrexate, steroids); thiopurine discontinuation, hospitalization or surgical intervention. A secondary outcome defined treatment failure as a change from remission to moderate or severe (not mild) in addition to the previously defined criteria.
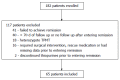
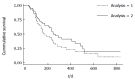
Results: Sixty-five of 182 patients in the PIBDNet registry met criteria for inclusion in this study. Forty-five of 65 (69%) of included patients achieved remission within 180 d of thiopurine initiation. For the primary outcome, 47% and 23% of patients remained in SFR at 6 and 12 mo. The mean thiopurine dose at initiation for the 65 included patients was 0.89 ± 0.31 mg/kg per day. Metabolite levels were obtained in 48% (31/65) of the included patients with a mean 6TG level of 258 pmole/8 × 10(8) RBC ± 147. For the secondary outcome, 65% and 42% of patients remained in SFR at 6 and 12 mo.
Conclusion: Thiopurines were less effective in maintaining remission for pediatric CD in this "real world" cohort than has been previously described. Variation in thiopurine dosing and metabolite measurement was found among practitioners.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Mercaptopurine; Pediatric; Remission; Thiopurines.
Figures
References
-
- Benchimol EI, Fortinsky KJ, Gozdyra P, Van den Heuvel M, Van Limbergen J, Griffiths AM. Epidemiology of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of international trends. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:423–439. - PubMed
-
- Kelsen J, Baldassano RN. Inflammatory bowel disease: the difference between children and adults. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14 Suppl 2:S9–S11. - PubMed
-
- Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, Ghali WA, Ferris M, Chernoff G, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Barkema HW, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:46–54.e42; quiz e30. - PubMed
-
- Present DH, Korelitz BI, Wisch N, Glass JL, Sachar DB, Pasternack BS. Treatment of Crohn‘s disease with 6-mercaptopurine. A long-term, randomized, double-blind study. N Engl J Med. 1980;302:981–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous