Nipple-areola complex reconstruction
- PMID: 25083492
- PMCID: PMC4115772
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2014.02.06
Nipple-areola complex reconstruction
Abstract
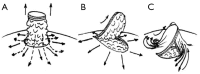
Nipple areolar reconstruction (NAC) was introduced since 1940s and evolved as parallel with breast reconstruction since era of breast cancer treatment. It consists of nipple and areolar reconstruction. Ideal reconstruction of the NAC requires symmetry in position, size, shape, texture, and pigmentation and permanent projection. There are many innovative ways to create a nipple and each method has its unique characteristics that apply to certain breast types. NAC reconstruction techniques comprises of composite nipple grafts, local flap, flaps with autologous graft augmentation, flaps with alloplastic augmentation and flaps with allograft augmentation. Areolar reconstruction by using skin grafting and tattooing are the easiest and most common techniques. With the evolution of techniques and technology, perhaps the newer methods of NAC reconstruction can produce promising long-lasting aesthetically acceptable result with minimal morbidity.
Keywords: Nipple areolar reconstruction; allograft; alloplastic; autologous graft; composite nipple grafts; tattooing.
Figures

References
-
- Few JW, Marcus JR, Casas LA, et al. Long-term predictable nipple projection following reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999;104:1321-4 - PubMed
-
- Evans KK, Rasko Y, Lenert J, et al. The use of calcium hydroxylapatite for nipple projection after failed nipple-areolar reconstruction: early results. Ann Plast Surg 2005;55:25-9; discussion 29 - PubMed
-
- Adams WM. Free transplantation of the nipples and areola. Surgery 1944;15:186
-
- Adams WM. Labial transplant for correction of loss of the nipple. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 1949;4:295-8 - PubMed
-
- Millard DR., Jr Nipple and areola reconstruction by split-skin graft from the normal side. Plast Reconstr Surg 1972;50:350-3 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
