Liver metastases induce reversible hepatic B cell dysfunction mediated by Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells
- PMID: 25085111
- PMCID: PMC4197561
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.3A0114-012RR
Liver metastases induce reversible hepatic B cell dysfunction mediated by Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells
Abstract
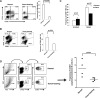
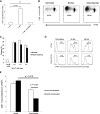
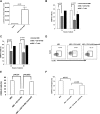
LM escape immune surveillance, in part, as a result of the expansion of CD11b+MC, which alter the intrahepatic microenvironment to promote tumor tolerance. HBC make up a significant proportion of liver lymphocytes and appear to delay tumor progression; however, their significance in the setting of LM is poorly defined. Therefore, we characterized HBC and HBC/CD11b+MC interactions using a murine model of LM. Tumor-bearing livers showed a trend toward elevated absolute numbers of CD19+ HBC. A significant increase in the frequency of IgM(lo)IgD(hi) mature HBC was observed in mice with LM compared with normal mice. HBC derived from tumor-bearing mice demonstrated increased proliferation in response to TLR and BCR stimulation ex vivo compared with HBC from normal livers. HBC from tumor-bearing livers exhibited significant down-regulation of CD80 and were impaired in inducing CD4(+) T cell proliferation ex vivo. We implicated hepatic CD11b+MC as mediators of CD80 down-modulation on HBC ex vivo via a CD11b-dependent mechanism that required cell-to-cell contact and STAT3 activity. Therefore, CD11b+MC may compromise the ability of HBC to promote T cell activation in the setting of LM as a result of diminished expression of CD80. Cross-talk between CD11b+MC and HBC may be an important component of LM-induced immunosuppression.
Keywords: B cells; STAT3; immunosuppression; liver.
© 2014 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Figures



References
-
- Burghardt S., Erhardt A., Claass B., Huber S., Adler G., Jacobs T., Chalaris A., Schmidt-Arras D., Rose-John S., Karimi K., Tiegs G. (2013) Hepatocytes contribute to immune regulation in the liver by activation of the notch signaling pathway in T cells. J. Immunol. 191, 5574–5582. - PubMed
-
- Connolly M. K., Bedrosian A. S., Malhotra A., Henning J. R., Ibrahim J., Vera V., Cieza-Rubio N. E., Hassan B. U., Pachter H. L., Cohen S., Frey A. B., Miller G. (2010) In hepatic fibrosis, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells acquire enhanced immunogenicity. J. Immunol. 185, 2200–2208. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Katz S. C., Pillarisetty V. G., Bleier J. I., Shah A. B., DeMatteo R. P. (2004) Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are insufficient to activate T cells. J. Immunol. 173, 230–235. - PubMed
-
- Valzasina B., Piconese S., Guiducci C., Colombo M. P. (2006) Tumor-induced expansion of regulatory T cells by conversion of CD4+CD25− lymphocytes is thymus and proliferation independent. Cancer Res. 66, 4488–4495. - PubMed
-
- Huang B., Pan P. Y., Li Q., Sato A. I., Levy D. E., Bromberg J., Divino C. M., Chen S. H. (2006) Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer Res. 66, 1123–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

