Actor and partner effects of perceived HIV stigma on social network components among people living with HIV/AIDS and their caregivers
- PMID: 25085478
- PMCID: PMC4312745
- DOI: 10.1177/1757975914537321
Actor and partner effects of perceived HIV stigma on social network components among people living with HIV/AIDS and their caregivers
Abstract
Background: Few studies have investigated the relationship between HIV stigma and social network components at the dyadic level. The objective of this study was to examine the actor and partner effects of perceived HIV stigma by people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHAs) and their caregivers on social network variables at the dyadic level.
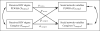
Method: An egocentric social network study was conducted among 147 dyads consisting of one PLWHA and one caregiver (294 participants) in Nanning, China. The actor-partner interdependence model (APIM) was used to analyze the relationships between perceived HIV stigma and social network components (network relations, network structures, and network functions) at the dyadic level.
Results: We found in this dyadic analysis that: (1) social network components were similar between PLWHAs and their caregivers; (2) HIV stigma perceived by PLWHAs influenced their own social network components, whereas this influence did not exist between caregivers' perceived HIV stigma and their own social network components; (3) a few significant partner effects were observed between HIV stigma and social network components among both PLWHAs and caregivers.
Conclusion: The interrelationships between HIV stigma and social network components were complex at the dyadic level. Future interventions programs targeting HIV stigma should focus on the interpersonal relationship at the dyadic level, beyond the intrapersonal factors.
Keywords: Actor-Partner Interdependence Model; China; HIV stigma; egocentric social network.
© The Author(s) 2014.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between perceived HIV stigma and quality of life at the dyadic level: the actor-partner interdependence model.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055680. Epub 2013 Feb 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383343 Free PMC article.
-
Network stigma towards people living with HIV/AIDS and their caregivers: An egocentric network study.Glob Public Health. 2015 Oct;10(9):1032-45. doi: 10.1080/17441692.2014.1003572. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Glob Public Health. 2015. PMID: 25642919 Free PMC article.
-
The impacts of depression and anxiety on quality of life among patients with HIV/AIDS and their spouses: testing dyadic dynamics using the actor-partner interdependence model.AIDS Care. 2019 Dec;31(12):1500-1508. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2019.1595676. Epub 2019 Mar 18. AIDS Care. 2019. PMID: 30884955
-
Heart Failure Care: Testing Dyadic Dynamics Using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM)-A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 9;19(4):1919. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19041919. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35206131 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-related perceived stigma and internalized stigma among people living with HIV/AIDS in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 23;19(10):e0309231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309231. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39441793 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Preoperative anxiety and associated factors among women admitted for elective obstetric and gynecologic surgery in public hospitals, Southern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 9;23(1):728. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05005-2. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37807071 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Individual and Network Factors in HIV Care Continuum Outcomes among PLWH: An Egocentric Network Study in Yunnan, China.AIDS Behav. 2025 Apr;29(4):1281-1293. doi: 10.1007/s10461-024-04602-w. Epub 2024 Dec 30. AIDS Behav. 2025. PMID: 39739286
-
The effects of beliefs about AIDS-related death on quality of life in Chinese married couples with both husband and wife infected with HIV: examining congruence using the actor-partner interdependence model.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017 Jun 17;15(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0703-z. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017. PMID: 28623928 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived Social Support and Associated Factors Among Adults Living with HIV/AIDS Attending ART Clinic at Public Hospitals in Gamo Zone, Southern Ethiopia 2021.HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2022 Mar 14;14:103-117. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S351324. eCollection 2022. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35341218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- China AIDS response progress report. Beijing: 2012. [accessed 22 October 2013]. The Ministry of Health of People's Republic of China. 2012 March 31. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/dataanalysis/knowyourresponse/countryprogressr....
-
- Brown L, Macintyre K, Trujillo L. Interventions to reduce HIV/AIDS stigma: what have we learned? AIDS Educ Prev. 2003;15:49–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

