Integrated genome-wide association, coexpression network, and expression single nucleotide polymorphism analysis identifies novel pathway in allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 25085501
- PMCID: PMC4127082
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-7-48
Integrated genome-wide association, coexpression network, and expression single nucleotide polymorphism analysis identifies novel pathway in allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis is a common disease whose genetic basis is incompletely explained. We report an integrated genomic analysis of allergic rhinitis.
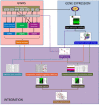
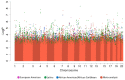
Methods: We performed genome wide association studies (GWAS) of allergic rhinitis in 5633 ethnically diverse North American subjects. Next, we profiled gene expression in disease-relevant tissue (peripheral blood CD4+ lymphocytes) collected from subjects who had been genotyped. We then integrated the GWAS and gene expression data using expression single nucleotide (eSNP), coexpression network, and pathway approaches to identify the biologic relevance of our GWAS.
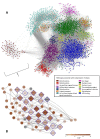
Results: GWAS revealed ethnicity-specific findings, with 4 genome-wide significant loci among Latinos and 1 genome-wide significant locus in the GWAS meta-analysis across ethnic groups. To identify biologic context for these results, we constructed a coexpression network to define modules of genes with similar patterns of CD4+ gene expression (coexpression modules) that could serve as constructs of broader gene expression. 6 of the 22 GWAS loci with P-value ≤ 1x10-6 tagged one particular coexpression module (4.0-fold enrichment, P-value 0.0029), and this module also had the greatest enrichment (3.4-fold enrichment, P-value 2.6 × 10-24) for allergic rhinitis-associated eSNPs (genetic variants associated with both gene expression and allergic rhinitis). The integrated GWAS, coexpression network, and eSNP results therefore supported this coexpression module as an allergic rhinitis module. Pathway analysis revealed that the module was enriched for mitochondrial pathways (8.6-fold enrichment, P-value 4.5 × 10-72).
Conclusions: Our results highlight mitochondrial pathways as a target for further investigation of allergic rhinitis mechanism and treatment. Our integrated approach can be applied to provide biologic context for GWAS of other diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Wallace DV, Dykewicz MS, Bernstein DI, Blessing-Moore J, Cox L, Khan DA, Lang DM, Nicklas RA, Oppenheimer J, Portnoy JM, Randolph CC, Schuller D, Spector SL, Tilles SA. The diagnosis and management of rhinitis: an updated practice parameter. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;7:S1–S84. - PubMed
-
- Feijen M, Gerritsen J, Postma DS. Genetics of allergic disease. Br Med Bull. 2000;7:894–907. - PubMed
-
- Davila I, Mjullol J, Ferrer M, Bartra J, del Cuvillo A, Montoro J, Jauregui I, Sastre J, Valero A. Genetic aspects of allergic rhinitis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009;7:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Ramasamy A, Curjuric I, Coin LJ, Kumar A, McArdle WL, Imboden M, Leynaert B, Kogevinas M, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Pekkanen J, Wjst M, Bircher AJ, Sovio U, Rochat T, Hartikainen AL, Balding DJ, Jarvelin MR, Probst-Hensch N, Strachan DP, Jarvis DL. A genome-wide meta-analysis of genetic variants associated with allergic rhinitis and grass sensitization and their interaction with birth order. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;7:996–1005. - PubMed
-
- Hindorff LA MJEBI, Morales J, Junkins HA, Hall PN, Klemm AK, Manolio TA, (European Bioinformatics Institute) A Catalog of Published Genome-Wide Association Studies. Available at: http://www.genome.gov/gwastudies Accessed September 19, 2013 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AI077439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL069167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES009581/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES011627/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL078885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RD831861/RD/ORD VA/United States
- AI070503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL079055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL101543/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- HL101651/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL105663/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 ES049019/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL65899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007048/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES007048/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI093538/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL085197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL065899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL072414/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES020801/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL066289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01ES011627/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL076647/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087680/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI061774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL087699/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES007048/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL075419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL064307/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL49596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL064313/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K08AI093538/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL066289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK064695/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES022719/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- AI079139/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL061768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL088133/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

