Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 25086665
- PMCID: PMC4191666
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3052
Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for pancreatic cancer
Abstract
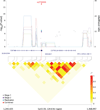
We performed a multistage genome-wide association study including 7,683 individuals with pancreatic cancer and 14,397 controls of European descent. Four new loci reached genome-wide significance: rs6971499 at 7q32.3 (LINC-PINT, per-allele odds ratio (OR) = 0.79, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.74-0.84, P = 3.0 × 10(-12)), rs7190458 at 16q23.1 (BCAR1/CTRB1/CTRB2, OR = 1.46, 95% CI 1.30-1.65, P = 1.1 × 10(-10)), rs9581943 at 13q12.2 (PDX1, OR = 1.15, 95% CI 1.10-1.20, P = 2.4 × 10(-9)) and rs16986825 at 22q12.1 (ZNRF3, OR = 1.18, 95% CI 1.12-1.25, P = 1.2 × 10(-8)). We identified an independent signal in exon 2 of TERT at the established region 5p15.33 (rs2736098, OR = 0.80, 95% CI 0.76-0.85, P = 9.8 × 10(-14)). We also identified a locus at 8q24.21 (rs1561927, P = 1.3 × 10(-7)) that approached genome-wide significance located 455 kb telomeric of PVT1. Our study identified multiple new susceptibility alleles for pancreatic cancer that are worthy of follow-up studies.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1374–1403. - PubMed
-
- Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1605–1617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 16491/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124908/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM074897/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010193/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 CA999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA062924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007142/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA173640/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA102701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U24 CA196171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA CP010193/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA140790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

