Obesity- and aging-induced excess of central transforming growth factor-β potentiates diabetic development via an RNA stress response
- PMID: 25086906
- PMCID: PMC4167789
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3616
Obesity- and aging-induced excess of central transforming growth factor-β potentiates diabetic development via an RNA stress response
Abstract
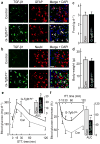
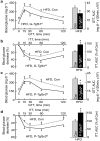
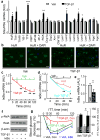
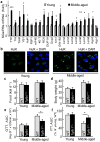
The brain, in particular the hypothalamus, plays a role in regulating glucose homeostasis; however, it remains unclear whether this organ is causally and etiologically involved in the development of diabetes. Here, we found that hypothalamic transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) production is excessive under conditions of not only obesity but also aging, which are two general etiological factors of type 2 diabetes. Pharmacological and genetic approaches revealed that central TGF-β excess caused hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance independent of a change in body weight. Further, using cell-specific genetic analyses in vivo, we found that astrocytes and proopiomelanocortin neurons are responsible for the production and prodiabetic effect of central TGF-β, respectively. Mechanistically, TGF-β excess induced a hypothalamic RNA stress response, resulting in accelerated mRNA decay of IκBα, an inhibitor of proinflammatory nuclear factor-κB. These results reveal an atypical, mRNA metabolism-driven hypothalamic nuclear factor-κB activation, a mechanism that links obesity as well as aging to hypothalamic inflammation and ultimately to type 2 diabetes.
Figures


Comment in
-
Metabolism: sugar on the brain.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Sep;15(9):563. doi: 10.1038/nrn3812. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25139270 No abstract available.
-
Atypical transforming growth factor-β signaling in the hypothalamus is linked to diabetes.Nat Med. 2014 Sep;20(9):985-7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3673. Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 25198046
References
-
- Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:415–445. - PubMed
-
- Muoio DM, Newgard CB. Obesity-related derangements in metabolic regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:367–401. - PubMed
-
- Mighiu PI, et al. Hypothalamic glucagon signaling inhibits hepatic glucose production. Nat Med. 2013;19:766–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

