A synthetic biology approach identifies the mammalian UPR RNA ligase RtcB
- PMID: 25087875
- PMCID: PMC4156904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.032
A synthetic biology approach identifies the mammalian UPR RNA ligase RtcB
Abstract
Signaling in the ancestral branch of the unfolded protein response (UPR) is initiated by unconventional splicing of HAC1/XBP1 mRNA during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In mammals, IRE1α has been known to cleave the XBP1 intron. However, the enzyme responsible for ligation of two XBP1 exons remains unknown. Using an XBP1 splicing-based synthetic circuit, we identify RtcB as the primary UPR RNA ligase. In RtcB knockout cells, XBP1 mRNA splicing is defective during ER stress. Genetic rescue and in vitro splicing show that the RNA ligase activity of RtcB is directly required for the splicing of XBP1 mRNA. Taken together, these data demonstrate that RtcB is the long-sought RNA ligase that catalyzes unconventional RNA splicing during the mammalian UPR.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

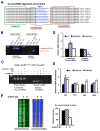


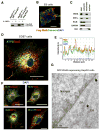
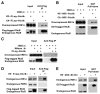

Comment in
-
Making ends meet: a role of RNA ligase RTCB in unfolded protein response.EMBO J. 2014 Dec 17;33(24):2887-9. doi: 10.15252/embj.201490425. Epub 2014 Nov 17. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25404664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta-Alvear D, Zhou Y, Blais A, Tsikitis M, Lents NH, Arias C, Lennon CJ, Kluger Y, Dynlacht BD. XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Molecular cell. 2007;27:53–66. - PubMed
-
- Back SH, Schroder M, Lee K, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ. ER stress signaling by regulated splicing: IRE1/HAC1/XBP1. Methods (San Diego, Calif) 2005;35:395–416. - PubMed
-
- Baltz AG, Munschauer M, Schwanhausser B, Vasile A, Murakawa Y, Schueler M, Youngs N, Penfold-Brown D, Drew K, Milek M, et al. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Molecular cell. 2012;46:674–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

