Puerarin alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting neuroinflammation in spinal cord
- PMID: 25089076
- PMCID: PMC4096058
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/485927
Puerarin alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting neuroinflammation in spinal cord
Abstract
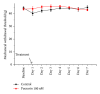
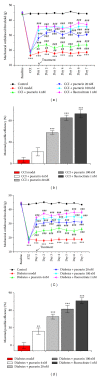
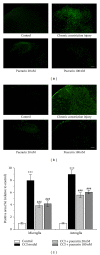
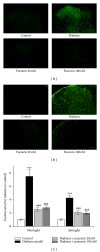
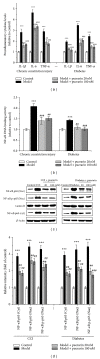
Neuropathic pain responds poorly to drug treatments, and partial relief is achieved in only about half of the patients. Puerarin, the main constituent of Puerariae Lobatae Radix, has been used extensively in China to treat hypertension and tumor. The current study examined the effects of puerarin on neuropathic pain using two most commonly used animal models: chronic constriction injury (CCI) and diabetic neuropathy. We found that consecutive intrathecal administration of puerarin (4-100 nM) for 7 days inhibited the mechanical and thermal nociceptive response induced by CCI and diabetes without interfering with the normal pain response. Meanwhile, in both models puerarin inhibited the activation of microglia and astroglia in the spinal dorsal horn. Puerarin also reduced the upregulated levels of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and other proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α, in the spinal cord. In summary, puerarin alleviated CCI- and diabetes-induced neuropathic pain, and its effectiveness might be due to the inhibition of neuroinflammation in the spinal cord. The anti-inflammation effect of puerarin might be related to the suppression of spinal NF-κB activation and/or cytokines upregulation. We conclude that puerarin has a significant effect on alleviating neuropathic pain and thus may serve as a therapeutic approach for neuropathic pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Danggui Sini decoction on neuropathic pain: experimental studies and clinical pharmacological significance of inhibiting glial activation and proinflammatory cytokines in the spinal cord .Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017 May;55(5):453-464. doi: 10.5414/CP202613. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28372633
-
Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting the TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in spinal microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 May 11;17(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1731-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32393298 Free PMC article.
-
Picroside II Attenuates CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats by Inhibiting Spinal Reactive Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Through the NF-κB Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018 May;43(5):1058-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2518-7. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29671236
-
Spinal interleukin-10 therapy to treat peripheral neuropathic pain.Neuromodulation. 2012 Nov-Dec;15(6):520-6; discussion 526. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1403.2012.00462.x. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Neuromodulation. 2012. PMID: 22672183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021 May 7;25(7):43. doi: 10.1007/s11916-021-00959-y. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021. PMID: 33961144 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of MicroRNA-221 Alleviates Neuropathic Pain Through Targeting Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Jul;59(3):411-20. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0748-1. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27059231
-
miR-873a-5p Targets A20 to Facilitate Morphine Tolerance in Mice.Front Neurosci. 2019 Apr 9;13:347. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00347. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31024249 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of three flavonoids from an ancient traditional Chinese medicine Radix puerariae on geriatric diseases.Brain Circ. 2018 Oct-Dec;4(4):174-184. doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_13_18. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Brain Circ. 2018. PMID: 30693344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Promise of Flavonoids to Combat Neuropathic Pain: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Implications.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 9;14:478. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00478. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32587501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrodia elata Blume Polysaccharides Attenuate Vincristine-Evoked Neuropathic Pain through the Inhibition of Neuroinflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jul 27;2021:9965081. doi: 10.1155/2021/9965081. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34366713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varrassi G, Müller-Schwefe G, Pergolizzi J, et al. Pharmacological treatment of chronic pain the need for CHANGE. Current Medical Research and Opinion. 2010;26(5):1231–1245. - PubMed
-
- Austin PJ, Moalem-Taylor G. The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. Journal of Neuroimmunology. 2010;229(1-2):26–50. - PubMed
-
- Vallejo R, Tilley DM, Vogel L, Benyamin R. The role of glia and the immune system in the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain Practice. 2010;10(3):167–184. - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK, Ji R. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: Distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2008;28(20):5189–5194. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

