The emerging profile of cross-resistance among the nonnucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- PMID: 25089538
- PMCID: PMC4147682
- DOI: 10.3390/v6082960
The emerging profile of cross-resistance among the nonnucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Abstract
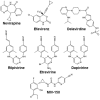
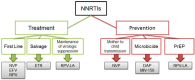
Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are widely used to treat HIV-1-infected individuals; indeed most first-line antiretroviral therapies typically include one NNRTI in combination with two nucleoside analogs. In 2008, the next-generation NNRTI etravirine was approved for the treatment of HIV-infected antiretroviral therapy-experienced individuals, including those with prior NNRTI exposure. NNRTIs are also increasingly being included in strategies to prevent HIV-1 infection. For example: (1) nevirapine is used to prevent mother-to-child transmission; (2) the ASPIRE (MTN 020) study will test whether a vaginal ring containing dapivirine can prevent HIV-1 infection in women; (3) a microbicide gel formulation containing the urea-PETT derivative MIV-150 is in a phase I study to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and acceptability; and (4) a long acting rilpivirine formulation is under-development for pre-exposure prophylaxis. Given their widespread use, particularly in resource-limited settings, as well as their low genetic barriers to resistance, there are concerns about overlapping resistance between the different NNRTIs. Consequently, a better understanding of the resistance and cross-resistance profiles among the NNRTI class is important for predicting response to treatment, and surveillance of transmitted drug-resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Telesnitsky A., Goff S. In: Reverse Transcriptase and the Generation of Retroviral DNA in Retroviruses. Coffin J., Hughes S., Varmus H., editors. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Plainview, NY, USA.: 1997. pp. 121–160. - PubMed
-
- Kohlstaedt L.A., Wang J., Friedman J.M., Rice P.A., Steitz T.A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992;26:1783–1790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical