Functional analysis of a novel ENU-induced PHD finger 11 (Phf11) mouse mutant
- PMID: 25091723
- PMCID: PMC4239810
- DOI: 10.1007/s00335-014-9535-x
Functional analysis of a novel ENU-induced PHD finger 11 (Phf11) mouse mutant
Abstract
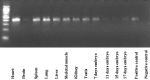
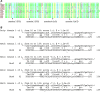
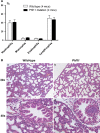
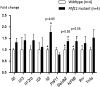
Previously, human genetic studies have shown association between polymorphisms within the gene encoding plant homeodomain zinc finger protein 11 (PHF11) and asthma-related phenotypes. Initial functional studies have suggested that PHF11 may be involved in the immune response through regulation of T cell activities. In order to study further the gene's functions, we have investigated the mouse Phf11 locus. We have established and characterised a mouse line harbouring a point mutation in the PHD domain of Phf11. Full-length mouse cDNA for Phf11 was obtained by applying rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE). All five exons encoding the PHD domain of Phf11 were directly sequenced in 3840 mouse DNA samples from the UK MRC Harwell ENU (N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea)-mutagenised DNA archive. Mice harbouring a valine to alanine substitution, predicted to have a significant functional impact on the PHD zinc finger domain, were re-derived. These Phf11 mutant mice were outcrossed to C3H mice and then backcrossed for ten generations in order to establish a congenic line harbouring the single point mutation in Phf11. Macroscopic examination, haematology and histological examination of lung structure revealed no significant differences between mutant and wild-type mice. After administration of lipopolysaccharide, the level of expression of Il2, NF-kB and Setdb2 were significantly increased in Phf11 mutant homozygous lungs compared to control littermates. Our results provide evidence that Phf11 can operate as a Th1 cell regulator in immune responses. Moreover, our data indicate that these mice may provide a useful model for future studies on Phf11.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad W, Irvine AD, Lam H, Buckley C, Bingham EA, Panteleyev AA, Ahmad M, McGrath JA, Christiano AM. A missense mutation in the zinc-finger domain of the human hairless gene underlies congenital atrichia in a family of Irish travellers. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63(4):984–991. doi: 10.1086/302069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

