Scrotal reconstruction using a superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap following Fournier's gangrene
- PMID: 25091799
- PMCID: PMC7950137
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12353
Scrotal reconstruction using a superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap following Fournier's gangrene
Abstract
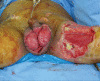
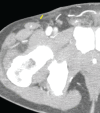
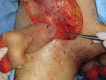
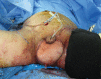
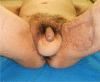
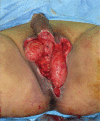
Fournier's gangrene is a type of necrotising fasciitis around the scrotum and perineum. Because of its aggressive nature, patients should be treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics and emergency, radical debridement during the acute phase. After recovering from the acute phase, reconstruction of the scrotal and perineal soft tissue defects is needed and is often challenging. Traditionally, various reconstruction methods have been used, including skin grafts, fasciocutaneous flaps and musculocutaneous flaps, each with its pros and cons. We successfully covered a wide scrotal defect using a superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap, which has not been previously reported for this indication. The design and operative technique are introduced in this study.
Keywords: Fournier's gangrene; SCIP; Scrotal defect.
© 2014 The Authors. International Wound Journal © 2014 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Scrotal reconstruction after Fournier's Gangrene using the superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator (SCIP) propeller flap: A case report.Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2024 Jul;69(4):320-325. doi: 10.1016/j.anplas.2024.05.001. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2024. PMID: 38866679
-
Pedicled Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery Perforator (SCIP) flap for perineo-scrotal reconstruction following Fournier's gangrene.ANZ J Surg. 2023 Jan;93(1-2):276-280. doi: 10.1111/ans.18066. Epub 2022 Oct 1. ANZ J Surg. 2023. PMID: 36181427
-
Reconstruction of penile skin loss by superficial circumflex iliac perforator (SCIP) pedicled flap after Fournier's gangrene.Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2024 May;69(3):217-221. doi: 10.1016/j.anplas.2023.06.012. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2024. PMID: 37429802
-
Therapeutic efficacy of combined superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap and bilateral pedicled scrotal flaps for perineal defects in male patients with extramammary Paget's disease.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2025 Apr;103:333-341. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2024.09.036. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2025. PMID: 40054293 Review.
-
[Plastic reconstruction of external genitalia after Fournier's gangrene].Urologe A. 2017 Oct;56(10):1289-1292. doi: 10.1007/s00120-017-0477-2. Urologe A. 2017. PMID: 28801729 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Reconstruction of Scrotal Skin Defects Using Bilobed Pudendal Flap.J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022 Oct-Dec;15(4):400-404. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_233_20. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022. PMID: 37035591 Free PMC article.
-
Crafting Contours: A Comprehensive Guide to Scrotal Reconstruction.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;14(2):223. doi: 10.3390/life14020223. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Fasciocutaneous Superomedial Thigh Flap in Reconstruction of Fournier Gangrene Defects.Eplasty. 2022 Jul 12;22:e26. eCollection 2022. Eplasty. 2022. PMID: 36000012 Free PMC article.
-
Fournier gangrene with concurrent multifocal necrotizing fasciitis: a systematic review and case report.Ann Coloproctol. 2023 Oct;39(5):421-426. doi: 10.3393/ac.2022.00192.0027. Epub 2022 May 26. Ann Coloproctol. 2023. PMID: 35615761 Free PMC article.
-
Peri-vulvar reconstruction using internal pudendal artery perforator flap in female Fournier's gangrene.Int Wound J. 2017 Dec;14(6):1378-1381. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12744. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Int Wound J. 2017. PMID: 28371369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eke N. Fournier's gangrene: a review of 1726 cases. Br J Surg 2000;87:718–28. - PubMed
-
- Chen SY, Fu JP, Chen TM, Chen SG. Reconstruction of scrotal and perineal defects in Fournier's gangrene. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2011;64:528–34. - PubMed
-
- Ersay A, Yilmaz G, Akgun Y, Celik Y. Factors affecting mortality of Fournier's gangrene: review of 70 patients. ANZ J Surg 2007;77:43–8. - PubMed
-
- Hsu H, Lin CM, Sun TB, Cheng LF, Chien SH. Unilateral gracilis myofasciocutaneous advancement flap for single stage reconstruction of scrotal and perineal defects. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2007;60:1055–9. - PubMed
-
- Atik B, Tan O, Ceylan K, Etlik O, Demir C. Reconstruction of wide scrotal defect using superthin groin flap. Urology 2006;68:419–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

