Oxidative protein folding: from thiol-disulfide exchange reactions to the redox poise of the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 25091901
- PMCID: PMC4312752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.037
Oxidative protein folding: from thiol-disulfide exchange reactions to the redox poise of the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
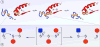
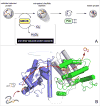
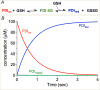
This review examines oxidative protein folding within the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum (ER) from an enzymological perspective. In protein disulfide isomerase-first (PDI-first) pathways of oxidative protein folding, PDI is the immediate oxidant of reduced client proteins and then addresses disulfide mispairings in a second isomerization phase. In PDI-second pathways the initial oxidation is PDI-independent. Evidence for the rapid reduction of PDI by reduced glutathione is presented in the context of PDI-first pathways. Strategies and challenges are discussed for determination of the concentrations of reduced and oxidized glutathione and of the ratios of PDI(red):PDI(ox). The preponderance of evidence suggests that the mammalian ER is more reducing than first envisaged. The average redox state of major PDI-family members is largely to almost totally reduced. These observations are consistent with model studies showing that oxidative protein folding proceeds most efficiently at a reducing redox poise consistent with a stoichiometric insertion of disulfides into client proteins. After a discussion of the use of natively encoded fluorescent probes to report the glutathione redox poise of the ER, this review concludes with an elaboration of a complementary strategy to discontinuously survey the redox state of as many redox-active disulfides as can be identified by ratiometric LC-MS-MS methods. Consortia of oxidoreductases that are in redox equilibrium can then be identified and compared to the glutathione redox poise of the ER to gain a more detailed understanding of the factors that influence oxidative protein folding within the secretory compartment.
Keywords: Disulfide exchange; Endoplasmic reticulum; Ero1; Glutathione; Oxidative protein folding; Peroxiredoxin; Protein disulfide isomerase; Quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase; Ratiometric mass spectrometry; Redox potential.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Anfinsen CB. Principles that Govern the Folding of Protein Chains. Science. 1973;181:223–230. - PubMed
-
- Riemer J, Bulleid N, Herrmann JM. Disulfide formation in the ER and mitochondria: two solutions to a common process. Science. 2009;324:1284–1287. - PubMed
-
- Hatahet F, Ruddock LW. Protein Disulfide Isomerase: A Critical Evaluation of Its Function in Disulfide Bond Formation. Antioxid Redox Signalling. 2009;11:2807–2850. - PubMed
-
- Braakman I, Bulleid NJ. Protein folding and modification in the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. Ann Rev Biochem. 2011;80:71–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

