Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone and anti-thyroglobulin antibody are independently associated with lesions in spinal cord in central nervous system demyelinating diseases
- PMID: 25093326
- PMCID: PMC4122347
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100672
Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone and anti-thyroglobulin antibody are independently associated with lesions in spinal cord in central nervous system demyelinating diseases
Abstract
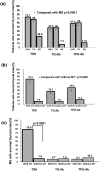
Transverse myelitis (TM) is associated with neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and multiple sclerosis (MS). Early recognition of useful parameters may be helpful to distinguish their difference. This retrospective study analyzed thyroid parameters from 243 serum samples (relapse = 128; remission = 115) of 178 patients with demyelinating diseases (NMO, n = 25; TM, n = 48; MS, n = 105). The relationship between thyroid and clinical parameters was analyzed. Patients with NMO and TM had a higher frequency of abnormal thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), anti-thyroglobulin antibodies (TG-Ab), and antithyroid peroxidase antibody (TPO-Ab) than MS patients (p<0.05). The level of TSH and TG-Ab returned to normal levels after administration of high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone (p<0.05). In 96 patients (NMO, n = 19; TM, n = 25; MS, n = 52) without treatment, serum levels of TSH, TG-Ab and TPO-Ab were significantly different between patients with and without myelitis (p<0.01). Patients positive for aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibodies showed higher abnormalities of TSH (p = 0.001), TG-Ab (p = 0.004) and TPO-Ab (p<0.0001) levels than AQP4 antibodies negative patients. Logistic regression analyses revealed independent relationships between TSH (odds ratio [OR] = 33.994; p<0.0001), TG-Ab (OR = 7.703; p = 0.017) and myelitis occurrence in 96 patients at the active stage. In 52 MS patients experiencing their first attack, MS patients with myelitis were associated with TSH abnormalities (OR = 42.778; p<0.0001). This study showed increased abnormalities of thyroid parameters in patients with NMO and TM than in MS patients. MS patients with myelitis also had greater TSH abnormality than in MS patients without myelitis. Abnormal TSH and TG-Ab were independently associated with myelitis occurrence in central nervous system demyelinating disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Li R, Qiu W, Lu Z, Dai Y, Wu A, et al. (2011) Acute transverse myelitis in demyelinating diseases among the Chinese. J Neurol 258: 2206–2213. - PubMed
-
- de Seze J, Lebrun C, Stojkovic T, Ferriby D, Chatel M, et al. (2003) Is Devic's neuromyelitis optica a separate disease? A comparative study with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 9: 521–525. - PubMed
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG (2006) Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 66: 1485–1489. - PubMed
-
- Munteis E, Cano JF, Flores JA, Martinez-Rodriguez JE, Miret M, et al. (2007) Prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disorders in a Spanish multiple sclerosis cohort. Eur J Neurol 14: 1048–1052. - PubMed
-
- Sakuma R, Fujihara K, Sato N, Mochizuki H, Itoyama Y (1999) Optic-spinal form of multiple sclerosis and anti-thyroid autoantibodies. J Neurol 246: 449–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

