Characteristics of Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- as a monophasic variant of serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 25093666
- PMCID: PMC4122451
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104380
Characteristics of Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- as a monophasic variant of serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
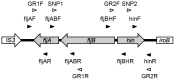
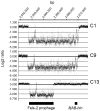
Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- (S. 4,[5]12:i:-) is believed to be a monophasic variant of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium). This study was conducted to corroborate this hypothesis and to identify the molecular and phenotypic characteristics of the S. 4,[5]12:i:- isolates in Japan. A total of 51 S. 4,[5]12:i:- isolates derived from humans, cattle, swine, chickens, birds, meat (pork), and river water in 15 prefectures in Japan between 2000 and 2010 were analyzed. All the S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates were identified as S. Typhimurium by two different polymerase chain reactions (PCR) for identification of S. Typhimurium. Of the 51 S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates, 39 (76.5%) harbored a 94-kb virulence plasmid, which is known to be specific for S. Typhimurium. These data suggest that the S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates are monophasic variants of S. Typhimurium. The flagellar phase variation is induced by three adjacent genes (fljA, fljB, and hin) in the chromosome. The results of PCR mapping of this region and comparative genomic hybridization analysis suggested that the deletion of the fljAB operon and its flanking region was the major genetic basis of the monophasic phenotype of S. 4,[5],12:i:-. The fljAB operon and hin gene were detectable in eight of the S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates with common amino acid substitutions of A46T in FljA and R140L in Hin. The introduction of these mutations into S. Typhimurium isolates led to the loss of selectability of isolates expressing the phase 2 H antigen. These data suggested that a point mutation was the genetic basis, at least in part, of the S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates. The results of phenotypic analysis suggested that the S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates in Japan consist of multiple distinct clones. This is the first detailed characterization of the S. 4,[5],12:i:- isolates derived from various sources across Japan.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, et al. (2010) The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Infect Dis 50: 882–889. - PubMed
-
- Grimont PAD, Grimont F, Bouvet P (2000) Taxonomy of the Genus Salmonella In: Wray C, Wray, A., etidor. Salmonella in Domestic Animals. Wallingford: CABI Publishing. pp. 1–17.
-
- Grimont P, Weil F (2007) Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed. World Health Organization Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella. Paris, France: Pasteur Institute.
-
- Dionisi AM, Graziani C, Lucarelli C, Filetici E, Villa L, et al. (2009) Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant strains of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium and Monophasic variant (S. 4,[5],12:i:-) isolated from human infections in Italy. Foodborne Pathog Dis 6: 711–717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

