An unusual piceatannol dimer from Rheum austral D. Don with antioxidant activity
- PMID: 25093985
- PMCID: PMC6271410
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules190811453
An unusual piceatannol dimer from Rheum austral D. Don with antioxidant activity
Abstract
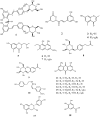
A novel dimer of piceatannol glycoside, named rheumaustralin (1) was isolated from the underground parts of the ethnomedicinal plant Rheum austral (Polygonaceae) collected from Tibet together with 17 known compounds, including rheumin (2), 2,5-dimethyl-7-hydroxychromone (3), 2,5-dimethylchromone-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (4), 7-hydroxy-2-(2'-hydroxypropyl)-5-methylchromone (5), torachrysone (6) torachrysone-8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (7), 4-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (8), amabiloside (9), N-trans-feruloyl tyramine (10), chrysophanol (11), aloe-emodin (12), emodin (13), physcion (14), physcion-1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (15), emodin-8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (16), D-catechin (17) and gallic acid (18). Their structures were determined by combined spectroscopic methods and by comparison of their spectral data with those reported in literature. Compounds 1-10 were tested for their ability to scavenge 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bao B., Alisa E.G. RHEUM Linnaeus. In: Li A., Bao B., Alisa E.G., Suk-pyo H., John M., Sergei L.M., Hideaki O., Chong-wook P., editors. Flora of China. Volume 5. Science Press & Missouri Botanical Garden; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2003. pp. 277–350.
-
- Zargar B.A., Masoodi M.H., Ahmed B., Ganie S.A. Phytoconstituents and therapeutic uses of Rheum emodi wall. ex Meissn. Food Chem. 2011;128:585–589. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.083. - DOI
-
- Liu B., Yang J., Wang S. The chemical constituents in rhubarb rhizomes and roots derived from Rheum emodi Wall. Huaxi Yaoxue Zazhi. 2007;22:33–35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical