Comparative evaluation of newborn bloodspot specimen cards by experienced laboratory personnel and by an optical scanning instrument
- PMID: 25095725
- PMCID: PMC8944415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.07.007
Comparative evaluation of newborn bloodspot specimen cards by experienced laboratory personnel and by an optical scanning instrument
Abstract
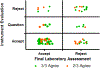
A major factor in determining the suitability of a dried blood spot (DBS) specimen is the subjective nature of evaluation by laboratory personnel. Using newborn screening DBS specimen cards as they were submitted to a public health NBS program, we conducted a systematic pilot study of DBS evaluation by multiple experienced laboratory personnel (ELP) and by an automated optical scanning instrument (OSI) (CardScan (tm), BSD Robotics). OSI confirmed the satisfactory status of all newborn DBS specimen cards that passed initial review by the first ELP. Among the questionable cards selected for further review, 58% passed multiple ELP consensus assessment, and 62% passed OSI evaluation. The overall agreement between ELP and OSI was 86%. Among questionable specimen cards, ELP and OSI were more strongly correlated when multiple ELP assessment was unanimous. We conclude that subjective assessment by ELP is essential and that OSI evaluation is a useful adjunct when ELP assessment does not reach consensus. OSI further allows the selection of optimal locations for punching DBS from unsatisfactory or questionable specimens, optimizing the quality of interim analyses that may be conducted while repeat specimens are being collected. Instrument evaluation of specimen cards would also be valuable as an independent reference method for training laboratory and specimen collection personnel. OSI technology merits further studies to confirm and extend our findings.
Keywords: Automation; Dried blood spots; Evaluation; Newborn bloodspot screening; Specimen quality; Training.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Hannon WH, Therrell BL, Overview of the History and Applications of Dried Blood Samples. in Lee MS and Wenkui L (Eds.), Dried Blood Spots Application and Techniques, John Wiley & Sons Inc. Hoboken, New Jersey: 2014, pp. 3–15 in press.
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Blood Collection on Filter Paper for Newborn Screening Programs; Standard—Sixth Edition. CLSI document NBS01-A6 (ISBN 1-56238-883-5 [Print]; ISBN 1-56238-884-3 [Electronic]). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087 USA, July 2013.
-
- Sherwin J, Web Conference on Unsatisfactory Newborn Screening Specimens: Interpretations, Studies and Current Trends. PowerPoint Presentation, 05/17/2005. www.cdc.gov/labstandards/nsqap_conferences_2005.html.
-
- Ontario Newborn Screening Program: Blood Spot Collection 2009. www.newbornscreening.on.ca.
-
- Luminex CardScan™ Software Installation and User Manual. © Luminex Corporation; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

