Rer1p regulates the ER retention of immature rhodopsin and modulates its intracellular trafficking
- PMID: 25096327
- PMCID: PMC4122963
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05973
Rer1p regulates the ER retention of immature rhodopsin and modulates its intracellular trafficking
Abstract
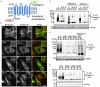
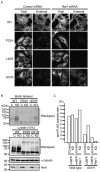
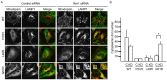
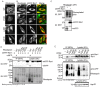
Rhodopsin is a pigment in photoreceptor cells. Some rhodopsin mutations cause the protein to accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), leading to photoreceptor degeneration. Although several mutations have been reported, how mutant rhodopsin is retained in the ER remains unclear. In this study, we identified Rer1p as a modulator of ER retention and rhodopsin trafficking. Loss of Rer1p increased the transport of wild-type rhodopsin to post-Golgi compartments. Overexpression of Rer1p caused immature wild-type rhodopsin to accumulate in the ER. Interestingly, the G51R rhodopsin mutant, which has a mutation in the first transmembrane domain and accumulates in the ER, was released to the plasma membrane or lysosomes in Rer1-knockdown cells. Consistent with these results, Rer1p interacted with both wild-type and mutant rhodopsin. These results suggest that Rer1p regulates the ER retention of immature or misfolded rhodopsin and modulates its intracellular trafficking through the early secretory pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Membrane protein retrieval from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER): characterization of the RER1 gene product as a component involved in ER localization of Sec12p.Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Nov;6(11):1459-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.11.1459. Mol Biol Cell. 1995. PMID: 8589449 Free PMC article.
-
Rer1p, a retrieval receptor for endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins, is dynamically localized to the Golgi apparatus by coatomer.J Cell Biol. 2001 Mar 5;152(5):935-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.5.935. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238450 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum localization of Sec12p is achieved by two mechanisms: Rer1p-dependent retrieval that requires the transmembrane domain and Rer1p-independent retention that involves the cytoplasmic domain.J Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;134(2):279-93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.2.279. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8707815 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodopsin Trafficking and Mistrafficking: Signals, Molecular Components, and Mechanisms.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;132:39-71. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26055054 Review.
-
Control of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator membrane trafficking: not just from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi.FEBS J. 2013 Sep;280(18):4396-406. doi: 10.1111/febs.12392. Epub 2013 Jul 5. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23773658 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyrate prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by T17M rhodopsin.Cell Biosci. 2014 Dec 4;4(1):75. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-75. eCollection 2014. Cell Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25530840 Free PMC article.
-
Protein quality control in the secretory pathway.J Cell Biol. 2019 Oct 7;218(10):3171-3187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201906047. Epub 2019 Sep 19. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31537714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cargo receptor Surf4 regulates endoplasmic reticulum export of proinsulin in pancreatic β-cells.Commun Biol. 2022 May 13;5(1):458. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03417-6. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35562580 Free PMC article.
-
Nedd4-2 Haploinsufficiency in Mice Impairs the Ubiquitination of Rer1 and Increases the Susceptibility to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Seizures.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jun 27;15:919718. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.919718. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35832397 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Bile Salt Export Pump (ABCB11) Interactome Employing Complementary Approaches.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 29;11(7):e0159778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159778. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27472061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aridor M. & Hannan L. A. Traffic jam: a compendium of human diseases that affect intracellular transport processes. Traffic 1, 836–851 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Aridor M. & Hannan L. A. Traffic jams II: an update of diseases of intracellular transport. Traffic 3, 781–790 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Griciuc A., Aron L. & Ueffing M. ER stress in retinal degeneration: a target for rational therapy? Trends Mol Med 17, 442–451 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Mendes H. F., van der Spuy J., Chapple J. P. & Cheetham M. E. Mechanisms of cell death in rhodopsin retinitis pigmentosa: implications for therapy. Trends Mol Med 11, 177–185 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Anukanth A. & Khorana H. G. Structure and function in rhodopsin. Requirements of a specific structure for the intradiscal domain. J Biol Chem 269, 19738–19744 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

