Juvenile xanthogranuloma: a rare benign histiocytic disorder
- PMID: 25097495
- PMCID: PMC4112258
- DOI: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40918
Juvenile xanthogranuloma: a rare benign histiocytic disorder
Abstract
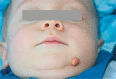
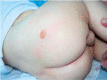
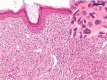
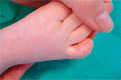
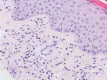
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a rare histiocytic disorder that typically affects children. The clinical presentation of this disease is characterized by single or, rarely, multiple yellow and brown skin nodules, most often found on the face and neck. Internal organ involvement has been sporadically observed in JXG and is associated with an increased risk of serious complications. We report two cases with a small and large nodular form of JXG.
Keywords: Touton cells; histiocytosis; juvenile xanthogranuloma; nodules.
Figures
References
-
- Dehner LP. Juvenile xanthogranulomas in the first two decades of life: a clinicopathologic study of 174 cases with cutaneous and extracutaneous manifestations. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:579–93. - PubMed
-
- Helwig EB, Hackney VC. Juvenile xanthogranuloma (nevo- xanthoendothelioma) Am J Pathol. 1954;30:625–6.
-
- Adamson NF. Congenital xanthoma multiplex in a child. Br J Dermatol. 1905;17:222–3.
-
- Cohen BA, Hood A. Xanthogranuloma: report on clinical and histological findings in 64 patients. Pediatr Dermatol. 1989;6:262–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
