Prospective assessment of a score for assessing basic critical-care transthoracic echocardiography skills in ventilated critically ill patients
- PMID: 25097797
- PMCID: PMC4113285
- DOI: 10.1186/2110-5820-4-12
Prospective assessment of a score for assessing basic critical-care transthoracic echocardiography skills in ventilated critically ill patients
Abstract
Background: We studied a score for assessing basic transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) skills exhibited by residents who examined critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
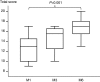
Methods: We conducted a prospective study in the 16 residents who worked in our medical-surgical ICU between 1 May 2008 and 1 November 2009. The residents received theoretical teaching (two hours) then performed supervised TTEs during their six-month rotation. Their basic TTE skills in mechanically ventilated patients were evaluated after one (M1), three (M3), and six (M6) months by two experts, who used a scoring system devised for the study. After scoring, residents gave their hemodynamic diagnosis and suggested a treatment.
Results: The 4 residents with previous TTE skills obtained a significantly higher total score than did the 12 novices at M1 (18 (16 to 19) versus 13 (10 to 15), respectively, P = 0.03). In the novices, the total score increased significantly during training (M1, 13 (10 to 14); M3, 15 (12 to 16); and M6, 17 (15 to 18); P < 0.001) and correlated significantly with the number of supervised TTEs (r = 0.68, P < 0.0001). In the overall population, agreement with experts regarding the diagnosis and treatment was associated with a significantly higher total score (17 (16 to 18) versus 13 (12 to 16), P = 0.002). A total score ≥ 19/20 points had 100% specificity (95% confidence interval, 79 to 100%) for full agreement with the experts regarding the diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusions: Our results validate the scoring system developed for our study of the assessment of basic critical-care TTE skills in residents.
Keywords: Basic critical-care echocardiography skills; Goal-oriented bedside echocardiography; Hemodynamic assessment; Intensive care unit; Non-cardiologist intensivists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acceleration of the learning curve for mastering basic critical care echocardiography using computerized simulation.Intensive Care Med. 2018 Jul;44(7):1097-1105. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5248-z. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Intensive Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29931488
-
Providing Transthoracic Echocardiography Training for Intensive Care Unit Trainees: An Educational Improvement Initiative.J Surg Educ. 2018 Sep-Oct;75(5):1342-1350. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Apr 9. J Surg Educ. 2018. PMID: 29650485 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic ability of hand-held echocardiography in ventilated critically ill patients.Crit Care. 2003 Oct;7(5):R84-91. doi: 10.1186/cc2360. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Crit Care. 2003. PMID: 12974974 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transoesophageal echocardiography in critical care.Minerva Anestesiol. 2006 Nov;72(11):891-913. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006. PMID: 17095988 Review.
-
Point-of-Care Echocardiography and Hemodynamic Monitoring in Cirrhosis and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in the COVID-19 Era.J Intensive Care Med. 2021 May;36(5):511-523. doi: 10.1177/0885066620988281. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Intensive Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33438491 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic impact of basic critical care echocardiography performed by residents after limited training.Ann Intensive Care. 2024 Jul 29;14(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13613-024-01354-7. Ann Intensive Care. 2024. PMID: 39073505 Free PMC article.
-
End-expiratory occlusion maneuver to predict fluid responsiveness in the intensive care unit: an echocardiographic study.Crit Care. 2018 Feb 8;22(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1938-0. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 29415773 Free PMC article.
-
Phantom model and scoring system to assess ability in ultrasound-guided chest drain positioning.Crit Ultrasound J. 2016 Dec;8(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13089-016-0038-8. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Crit Ultrasound J. 2016. PMID: 26888754 Free PMC article.
-
Transpulmonary thermodilution: advantages and limits.Crit Care. 2017 Jun 19;21(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1739-5. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28625165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beaulieu Y. Bedside echocardiography in the assessment of the critically ill. Crit Care Med. 2007;4(5 Suppl):S235–S249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

