Germline mutations in the PAF1 complex gene CTR9 predispose to Wilms tumour
- PMID: 25099282
- PMCID: PMC4143912
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5398
Germline mutations in the PAF1 complex gene CTR9 predispose to Wilms tumour
Abstract
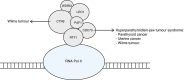
Wilms tumour is a childhood kidney cancer. Here we identify inactivating CTR9 mutations in 3 of 35 Wilms tumour families, through exome and Sanger sequencing. By contrast, no similar mutations are present in 1,000 population controls (P<0.0001). Each mutation segregates with Wilms tumour in the family and a second mutational event is present in available tumours. CTR9 is a key component of the polymerase-associated factor 1 complex which has multiple roles in RNA polymerase II regulation and is implicated in embryonic organogenesis and maintenance of embryonic stem cell pluripotency. These data establish CTR9 as a Wilms tumour predisposition gene and suggest it acts as a tumour suppressor gene.
Figures


References
-
- Pritchard-Jones K. et al. Treatment and outcome of Wilms’ tumour patients: an analysis of all cases registered in the UKW3 trial. Ann. Oncol. 23, 2457–2463 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Rahman N. et al. Evidence for a familial Wilms' tumour gene (FWT1) on chromosome 17q12-q21. Nat. Genet. 13, 461–463 (1996). - PubMed
-
- McDonald J. M. et al. Linkage of familial Wilms' tumor predisposition to chromosome 19 and a two-locus model for the etiology of familial tumors. Cancer Res. 58, 1387–1390 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

